In short
- According to a new market report on the topic, the number of global satellite IoT subscribers reached 5 million in 2021.
- Three key developments to watch for in the coming years: The rise of low Earth orbit (LEO)-based networks, the adoption of hybrid satellite-terrestrial connectivity, and the entry of tech giants as operators.
- The market is expected to grow to $1 billion by 2026 with the competitive intensity remaining extremely high.
Why it matters
- Organizations previously unable to connect to IoT solutions in remote areas due to a lack of coverage and cost issues now have various feasible solutions.
Despite being used for asset tracking and remote telemetry application since the late 70s, satellite connectivity in the M2M/IoT space has historically been considered a last resort alternative to terrestrial networks, mostly due to its higher costs and low-cost legacy-solution power efficiency. More recently, with the healthy growth of the IoT market and the coverage limitations of terrestrial networks, there has been a renewed interest in satellite-based IoT connectivity.
In the past 4 years, at least 13 start-ups and seven incumbent satellite operators have announced plans to deploy or have commercially launched satellite IoT networks that promise to deliver low-power, low-cost connectivity to IoT devices directly from space. Unlike terrestrial networks that cover only about 15%–20% of the planet’s surface, satellite networks can provide coverage to nearly all of the Earth’s surface and help accommodate the increasing IoT connectivity needs in isolated or inaccessible areas. With the demand for IoT solutions continuing to grow, IoT Analytics believes satellite connectivity will play an increasingly important role in the future of IoT, although satellite IoT will remain a niche service in the coming years compared to the entire IoT market.
Market overview: The state of satellite IoT connectivity in 2022
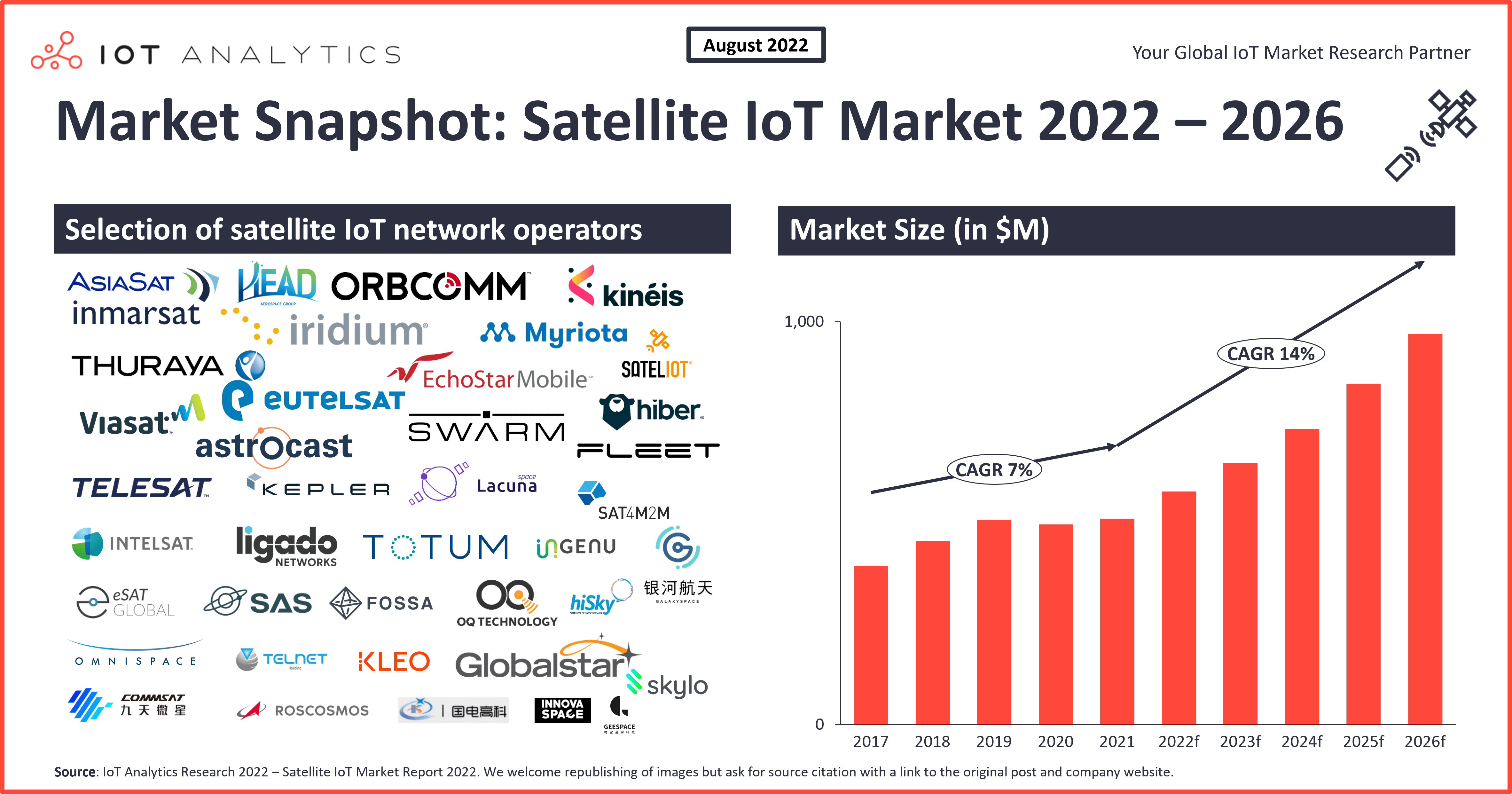
According to IoT Analytics’ Satellite IoT Connectivity Market Report 2022–2026, the number of Satellite IoT connectivity subscribers crossed 5 million in 2021.
Today, only 2% of the global Satellite Connectivity Market (in USD) relates to Satellite IoT Connectivity revenues. The bulk of satellite revenues today still represent voice communications for remote workers and represent first responders and internet connectivity services for consumers and businesses in remote areas. However, with satellite IoT connectivity revenues growing 14 times faster than traditional satellite connectivity revenue, IoT is coming up as a category.
Incumbent Satellite operators such as Inmarsat, Iridium, ORBCOMM, and Globalstar contribute to more than 80% of global satellite IoT connectivity revenues. However, emerging start-ups offering low-power and low-cost IoT connectivity through LEOs—based small satellite constellations—are expected to gain ground and account for approximately 20% of the global market by 2026.
As the market is rebuilding, we identified three key developments that will likely accelerate the growth of the satellite IoT market from a 7% CAGR in the previous years to a 14% CAGR in the coming years. Global revenue is expected to surpass 1 billion USD by 2026.
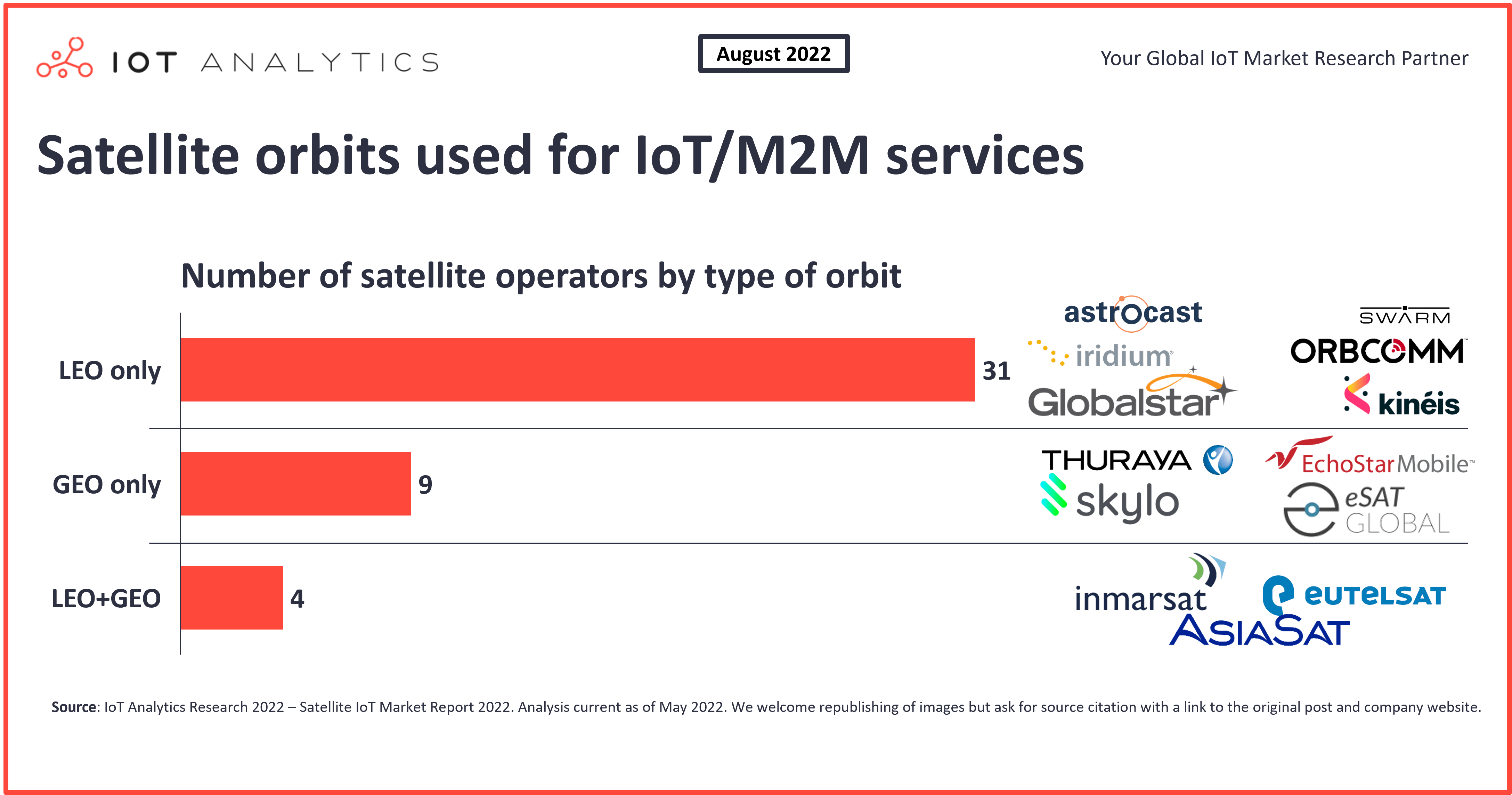
Development 1: The rise of LEO-based satellite IoT networks
According to IoT Analytics’ Satellite IoT Connectivity Market Report 2022–2026, satellite IoT connectivity based on LEO constellations will grow by 25% CAGR between 2022–2026. Most of the new satellite IoT networks announced and deployed in the past few years leverage LEOs. We identified two key reasons for the higher adoption rate of LEO-based deployment.
- LEO are better suited to low-power communications. LEO satellites are deployed at 200 km or lower. A shorter distance to Earth means lower signal propagation losses (estimated at approximately 25 dB less than with GEO), which reduce the user equipment’s power requirements and make it ideal for communication with low-power IoT devices.
- LEO constellations enable faster design and deployment at a low cost. Today, most LEO satellites for IoT are built leveraging CubeSat technology, which allows companies to mass-produce components and offer commercial off-the-shelf parts. It drastically reduces the cost and time to design and develop satellites. The combination of CubeSats and LEO today represents the quickest and most cost-effective way to build and deploy a satellite constellation for IoT. It has become the preferred option for incumbent satellite operators and NewSpace start-ups that are launching satellite IoT connectivity services.
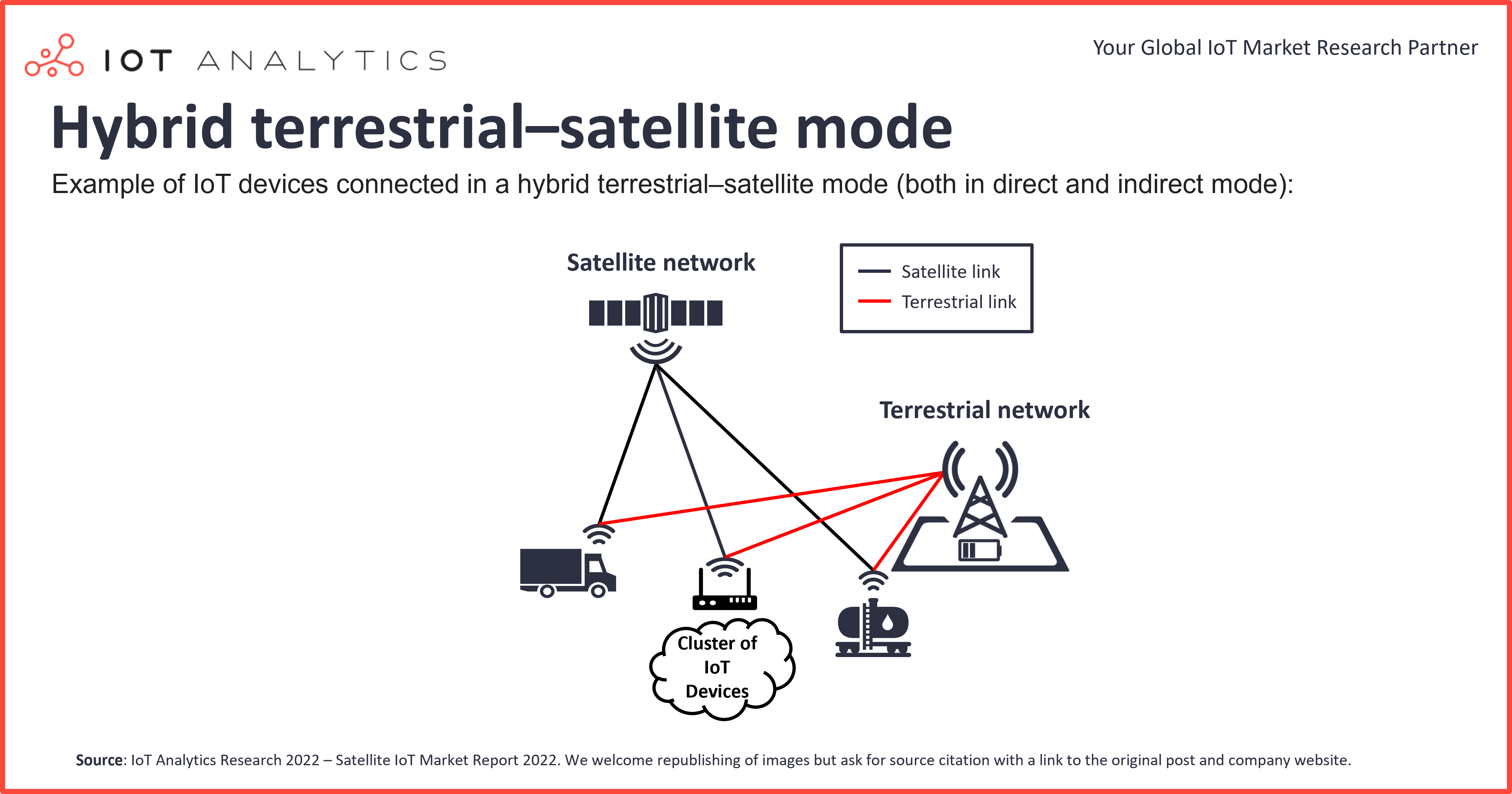
Development 2: The adoption of hybrid satellite-terrestrial connectivity
Partnership and collaboration are key in IoT deployment, as we can see in the satellite IoT connectivity ecosystem. Terrestrial and satellite IoT network operators are increasingly partnering to offer hybrid connectivity solutions, for example, Kinéis and Deutsche Telekom (Kinéis’ KIM 1 module is now certified by Deutsche Telekom and can be used by the latter’s customers in hybrid cellular-satellite solutions).
The solution enables IoT devices to use terrestrial connectivity (e.g., cellular) as their primary option and switch to satellites when moving to areas with no terrestrial network coverage. The solution requires two different RF chipsets embedded in the end-user device or satellite terminal.
Furthermore, new technologies that provide terrestrial and satellite connectivity through a single communication RF chipset are emerging. For example, the LoRa Edge LR1120 chipset supports Sub-GHz LoRa, SATCOM S-band, and 2.4 GHz Lora.
However, the single communication RF chipset supporting terrestrial and satellite connectivity can also be implemented on existing IoT devices through a firmware upgrade with no or minimal hardware changes, allowing vendors to leverage existing certifications, devices, and ecosystems. For example, Sateliot and OQ have developed similar solutions that enable existing NB–IoT devices to communicate via satellite, requiring only a firmware update to the devices without necessitating any changes to the hardware or antenna.
Development 3: The entry of tech giants as LEO-based broadband satellite operators
LEO-based connectivity is a new frontier. To capitalize on this opportunity, tech giants such as Starlink by SpaceX or Project Kuiper by Amazon are deploying LEO constellations for broadband internet connectivity. These constellations do not directly address the IoT market. However, from a technical standpoint, it could eventually represent a solid option for customers that need both high bandwidth and low bandwidth connectivity applications (e.g., vessels/container ships or remote industrial sites) and become a strong competitor for those companies focusing on satellite backhauling for IoT. For example:
- Connected Farms Pty Ltd, an Australian licensed telecommunications carrier, will launch a pilot project using Starlink’s backhaul service to provide connectivity fence to fence on farms for technologies connecting robotics, agriculture IoT, mobile phones, and home offices.
- Last year, in 2021, SpaceX acquired Swarm, whose target market is those requiring low-cost IoT connectivity.
The outlook for satellite IoT: A growing market with a high competitive intensity
As the market continues to grow towards $1 billion in market size, the sweet spot for satellite IoT connectivity remains deployments in remote and isolated areas. Satellite connectivity competes with other terrestrial connectivity options everywhere else (and is predominantly more expensive). Therefore, the total satellite IoT market size will remain a fraction of the entire IoT market for the foreseeable future.
At the same time, increasing competition in the satellite IoT market and the continuous erosion of IoT connectivity prices (and thus revenue margins) risk eating up the substantial CAPEX required for satellite operators as they build up satellite networks. Hence, it is our prediction that some of the new satellite operators will fail to sustain their businesses and may be forced to change their business model to survive. Some of these struggles are already visible. For example, Hiber, which was among the first NewSat companies to commercially launch satellite IoT connectivity services, recently dropped its plans to complete its constellation to focus on providing vertical IoT solutions (Astrocast then acquired Hiber in May 2022).
Definition of Satellite IoT
“Satellite IoT refers to the use of satellite communication networks and services to connect terrestrial IoT sensors and IoT end-nodes to a server (e.g., in a public or private cloud), either in conjunction with or as an alternative to terrestrial communication networks.”
More information and further reading
For more insights, check out our coverage of the Satellite IoT Connectivity Market:

Satellite IoT Market Report 2022-2026
119-page report detailing the satellite IoT market, including market share, use cases, and technical details.
Download the sample to learn more about the report structure, companies included, and see additional data points.
Related publications
You may be interested in the following publications:
Related market data
You may be interested in the following IoT market data products:
- Global Cellular IoT Module and Chipset Tracker and Forecast
- Global Cellular IoT Connectivity and LPWA Tracker and Forecast
Related articles
You may also be interested in the following recent articles:
- 5 things to know about the LPWAN market in 2021
- The rise of the IoT semiconductor
- The Leading 5G IoT Use Cases
Are you interested in continued IoT coverage and updates?
Subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter to stay up-to-date on the latest trends shaping the IoT markets. For complete enterprise IoT coverage with access to all of IoT Analytics’ paid content & reports including dedicated analyst time check out the Enterprise subscription.
