Updated April 2022: IoT Analytics published a more recent blog on: 55+ emerging IoT technologies you should have on your radar (2022 update)
There are hundreds of software, hardware and connectivity technologies that are relevant for IoT-type projects.
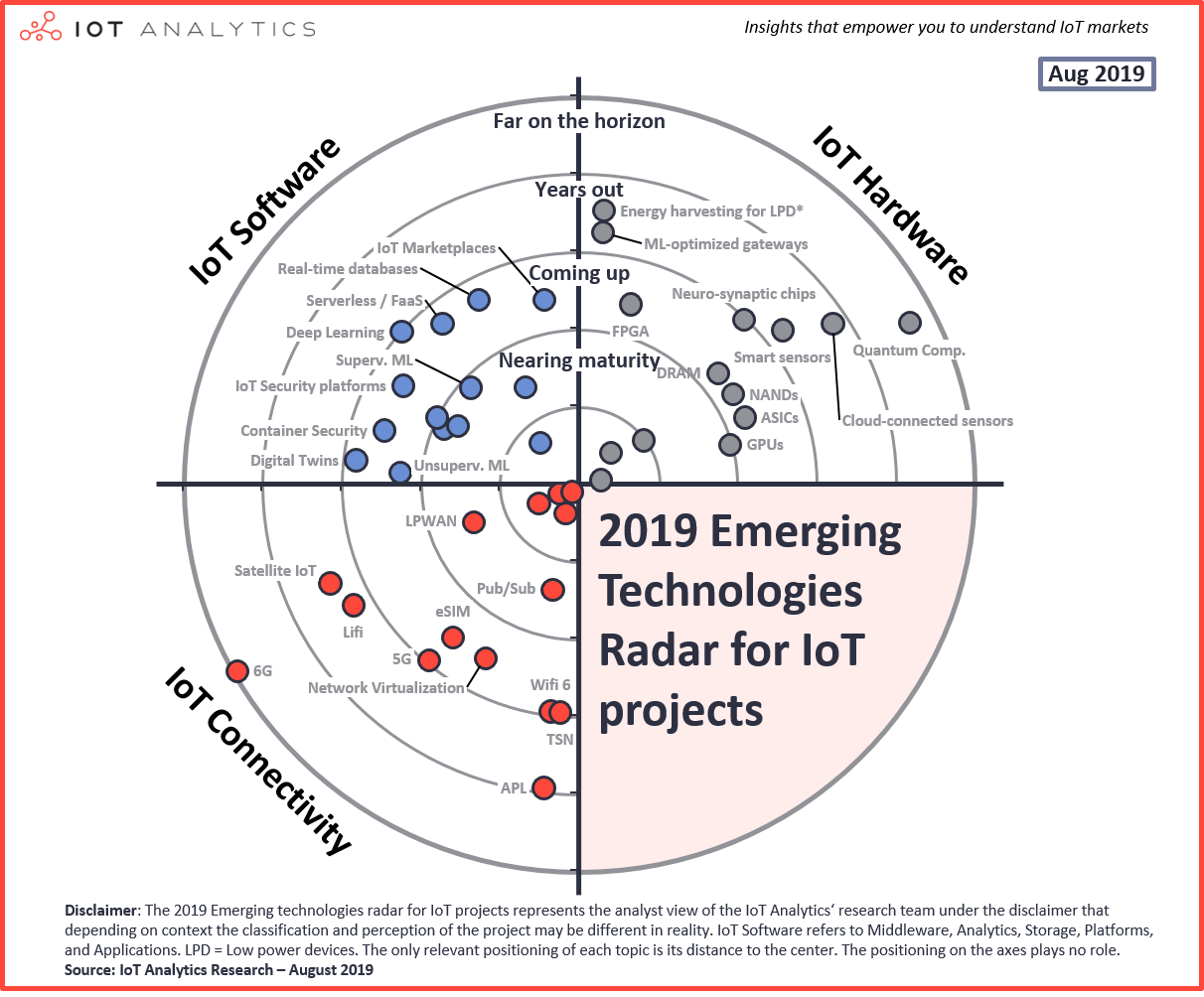
As part of the “State of the IoT – Summer 2019 Update”, the analyst team at IoT Analytics handpicked 43 of the most promising technologies that are relevant to IoT projects around the globe. The team ranked the IoT technologies according to their perceived maturity (based on expert interviews, vendor briefings, secondary research, and conference attendances).
The resulting Emerging IoT Technologies Radar serves as a guide for anyone working in IoT-type environments and projects to understand what technologies they should be watching, evaluating, and perhaps deploying. Many of the topics highlighted on the radar are discussed in much more depth in the State of the IoT 2019 Q1/Q2 Update report.
Here is the complete list of all software, hardware, and connectivity IoT technologies (each ranked by maturity):
A. IoT Software Technologies
| # | Technology | Description | Classification | Typical vendor(s) or solutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cloud computing | Using a network of remote servers to store, manage, and process data. | Fairly Mature | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Alibaba Aliyun |
| 2 | IoT Platforms | Form of modular software that allow easy connection of various IoT devices & other value-added functionality (e.g., remote device management, application enablement, analytics) | Nearing maturity | AWS IoT, Microsoft Azure IoT, PTC Thingworx |
| 3 | Edge analytics | Collection and analysis of data at the sensor, device, gateway or edge data center rather than waiting for the data to be sent back to a remote cloud. | Nearing maturity | AWS IoT Greengrass, Microsoft IoT Edge, Foghorn, Crosser |
| 4 | IoT-based streaming analytics | Real time processing of streaming of data from IoT devices | Nearing maturity | Cloud vendor solutions, Hortonworks Dataflow, SAS, Software AG |
| 5 | Supervised machine learning | ML method where training data for the algorithm includes desired outputs. | Nearing maturity | Uptake, Sparkcognition, Senseye |
| 6 | Unsupervised machine learning | ML method where training data for the algorithm does not include the desired outputs. | Nearing maturity | Uptake, Sparkcognition, Darktrace |
| 7 | Containers | Containers are processes with their own virtual resources and filesystems (memory, CPU, disk, etc.), isolated from other applications and containers | Nearing maturity | Docker, Kubernetes, OpenShift |
| 8 | IoT Marketplaces | A one-stop click-and-buy-store, offering complete Internet of Things solutions ready to deploy smart applications including hardware, software and cloud connection. | Coming up | PTC, Siemens, ABB, Schneider Electric, Inductive Automation |
| 9 | Digital Twins | Digital representation of physical assets, processes, systems and devices | Coming up | GE, Azure, Siemens, Honeywell, Emerson |
| 10 | Container Security | Solutions that protect the integrity of containers | Coming up | Cloud Vendor Solutions, Palo Alto Networks |
| 11 | IoT Security platforms | Platform offering security solutions for any IoT device class | Coming up | Mocana, Bayshore Networks, Device Authority |
| 12 | Real-time database | Database that uses real-time processing to handle constantly changing workloads | Coming up | MongoDB, Counchbase |
| 13 | Serverless / FaaS | Developing, running, and managing application functionalities without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure associated with developing and launching an application | Coming up | AWS Lamda, IBM OpenWhisk, Google Cloud Functions |
| 14 | Deep Learning | Part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks | Coming up | TensorFlow, Apache Mahout, Caffe, Deepmind, CuriousAI |
B. IoT Hardware Technologies
| # | Technology | Description | Classification | Typical vendor(s) or solutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CPU | Central processing unit | Fairly mature | Intel, HPE, AMD |
| 2 | Security chips | Security-enhancing low-powered modules, include various security-sensitive functions | Fairly mature | Apple, Alphabet |
| 3 | Edge gateways | Physical devices that serve as the connection point between the cloud and controllers, sensors and intelligent devices | Fairly mature | Dell, HPE |
| 4 | GPUs | Graphic processing unit | Coming up | NVIDIA, AMD, Asus, Intel |
| 5 | NAND | Non-volatile flesh memory | Coming up | Micron, Samsung, Toshiba |
| 6 | ASIC | Application-specific integrated circuit | Coming up | Fujitsu, Honeywell, Advanced Linear Devices |
| 7 | DRAM | Dynamic random-access memory | Coming up | Samsung, Micron, SK Hynics |
| 8 | FPGA | Field programmable gate array | Coming up | Xilinx, Intel, Altera |
| 9 | Neuro-synaptic chip | Brain-inspired computer chip, in which transistors simulate neurons and synapses | Coming up | IBM |
| 10 | Smart sensors | Sensors that take some predefined action when they sense the appropriate input | Years out | Texas Instruments, TE Connectivity, Broadcom |
| 11 | ML-optimized gateways | Controllers that are optimized for ML algorithms | Years out | Adlink, Intel |
| 12 | Energy harvesting for LPD | Supplying electricity to LPDs from one or several forms of available energy from the ambient environment instead of using disposable batteries or a connection to the electricity grid | Years out | STMicroelectronics, ABB |
| 13 | Cloud-connected sensors | Sensors that are sending data directly to the cloud | Years out | Schneider Electric |
| 14 | Quantum computing | Computation using quantum-mechanical phenomena e.g., superposition entanglement | Far on the horizon | IBM, Microsoft, Rigetti |
C. IoT Connectivity Technologies
| # | Technology | Description | Classification | Typical vendor(s) or solutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WLAN | Wireless Local Area Networks, includes Wi-Fi and its different versions | Fairly mature | Cisco, Aruba, Extreme Networks |
| 2 | WPAN | Wireless Personal Area Networks, incl. very short-range (up to ~100 m) connectivity technologies (e.g. BLE, Zigbee) | Fairly mature | DiGi Int., NXP Semiconductors, Silicon Labs |
| 3 | Cellular IoT (2G/3G/4G) | Provides connectivity to IoT applications via traditional cellular networks | Fairly mature | China Mobile, Vodafone, Orange |
| 4 | WNAN | Wireless Neighborhood Area Networks, includes medium-range (~500-2,000 km) mesh connectivity technologies based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard (e.g. Wi-SUN) | Fairly mature | Itron/Silver Spring Networks, Wirepas |
| 5 | LPWAN | Low-Power Wide-Area connectivity for IoT applications (e.g. Sigfox, LoRa, NB-IoT, LTE-M) | Nearing maturity | Semtech, Sigfox |
| 6 | Pub/Sub | Form of asynchronous service-to-service comm. used in IoT messaging protocols e.g. MQTT, XMPP | Nearing maturity | AWS, Google Cloud, PubNub |
| 7 | eSIM | A SIM-card embedded into mobile devices that enables remote SIM provisioning, allowing storing of multiple operator profiles simultaneously and switching between them remotely. | Coming up | ST Microelectronics, Gemalto, Giesecke & Devrient, ARM |
| 8 | Network Virtualization | Abstracts network elements & resources into a logical virtual network that runs independently on top of a physical network | Coming up | Oracle, VMWare, Juniper Networks |
| 9 | 5G | The fifth generation of cellular networks, commercially launched in 2019 | Coming up | Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia |
| 10 | Wifi 6 | The newest version of the Wi-Fi protocol, also known as IEE 802.11ax | Coming up | Qualcomm, Cisco, Huawei |
| 11 | TSN | Time-Sensitive Networking is a set of standards defined by IEEE for the time-sensitive transmission of data over deterministic Ethernet networks | Coming up | ABB, Bosch, Cisco, Siemens |
| 12 | Lifi | Wireless communication technology that uses light to transmit data. | Years out | Panasonic, Oledcomm, Philips |
| 13 | Satellite IoT | Provides connectivity to IoT applications via satellite networks | Years out | Iridium, Inmarsat, Eutelsat |
| 14 | APL (Advanced Physical Layer) | Developing industrial Ethernet standard that seeks to leverage the work of the IEEE 802.3cg (10BASE-T1L) task force to achieve a single twisted-pair industrial Ethernet standard for hazardous areas | Years out | Pepperl+Fuchs, Endress+Hauser, Analog Devices |
| 15 | 6G | The sixth generation of cellular networks | Far on the horizon | Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia |
What the radar measures and what it does not measure?
Technology maturity. The radar shows a subjective measure of maturity as put together by the analyst team at IoT Analytics. The maturity scores are developed based on expert interviews, vendor briefings, secondary research, and conference attendances. The radar is targeted at IoT practitioners that deploy IoT.
The Internet of Things. IoT Analytics defines the Internet of Things as a network of internet-enabled physical objects. Objects that become internet-enabled (IoT devices) typically interact via embedded systems, some form of network communications, as well as a combination of edge and cloud computing. The data from IoT-connected devices is often (but not exclusively) used to create novel end-user applications. Connected personal computers, tablets, and smartphones are not considered IoT, although these may be part of the solution setup. Devices connected via extremely simple connectivity methods such as RFID or QR-codes are not considered IoT devices.
Relevance of individual technologies. Not every technology is relevant for a given IoT context. Some technologies may be purely used in specific IoT settings (e.g., LPWAN for remote, low-power applications), others are used in a variety of settings and IoT only plays a minor role (e.g., Cloud computing which is also used in many non-IoT scenarios). IoT Analytics is aware that there are many more technologies out there that could be highlighted in such a radar.
Other selected research findings
In addition to the 2019 Emerging Technologies Radar, the 96-page “State of the IoT” report presents 67 current insights on the IoT market, including market breakdowns by industry, region and tech stack. The report also includes an IoT-focused investment and M&A analysis, a look at adjacent technologies, and gives insights from major IoT-focused conferences. This is a small selection of other insights:
- IoT technologies often take more than a decade to move towards the center of the emerging technologies radar. The typical technologies depicted here take roughly 12 years to move from being “far on the horizon” to becoming so mature and widely adopted that IoT Analytics considers them “mainstream” (in case a technology does become mainstream which is not always the case). Cloud computing, for example, took ~12 years from being far on the horizon to being considered “mainstream” for IoT settings (Note: AWS was first launched in 2006). Research on 5G was initiated in 2012 and was considered far on the horizon at that time. It has moved to the “Coming up” level now and is expected to hit mainstream for IoT applications in the 2024-2025 timeframe (~also 12 years later). One should note though that some technologies do mature quicker than others. Research on 6G started in 2019, by the way.
- Digital/IoT markets are currently affected by the global slowdown. IoT vendors are lowering their outlook while technology users are (partially) reducing CAPEX. At the same time, shifting supply chains and skill shortages are becoming key inhibitors to further growth in IoT.
- Lower growth going forward. IoT Analytics expects IoT markets to grow 30% in the medium-run (next 2 years) and 32% in long-run (5 years thereafter). The market is expected to cross the $1trillion mark in 2025.
- Manufacturing/Industrial hit the hardest. The global slowdown is currently mostly a manufacturing slowdown with Automotive and Machinery hit the hardest and with weakest outlook. Chemicals/Pharma and Food&Beverages are holding up the best.
- Analytics/AI driving the market. Companies are doubling down on their Analytics/AI investments which is why we expect this area of the tech stack to be the only one that will see a growth increase.
- US startups dominate large IoT funding rounds. Top recent IoT investments focus on cybersecurity (13%) and IoT connectivity (13%) – mostly in the US (45%), followed by Israel (10%) and China (10%).
Further reading
The Emerging IoT Technologies Radar discussed in this article is explored in further depth, in the 96-page State of the IoT 2019 Q1/Q2 Update report. The report takes a deeper look at the IoT market and provides 67 insights across the IoT tech stack, adjacent technologies, investments and M&A, and conference highlights.
A sample of the report and the database can be downloaded here.
Interested in continued IoT coverage and updates?
Subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter to stay up-to-date on the latest trends shaping the IoT markets. For complete enterprise IoT coverage with access to all of IoT Analytics’ paid content & reports including dedicated analyst time check out our Enterprise subscription.