In short
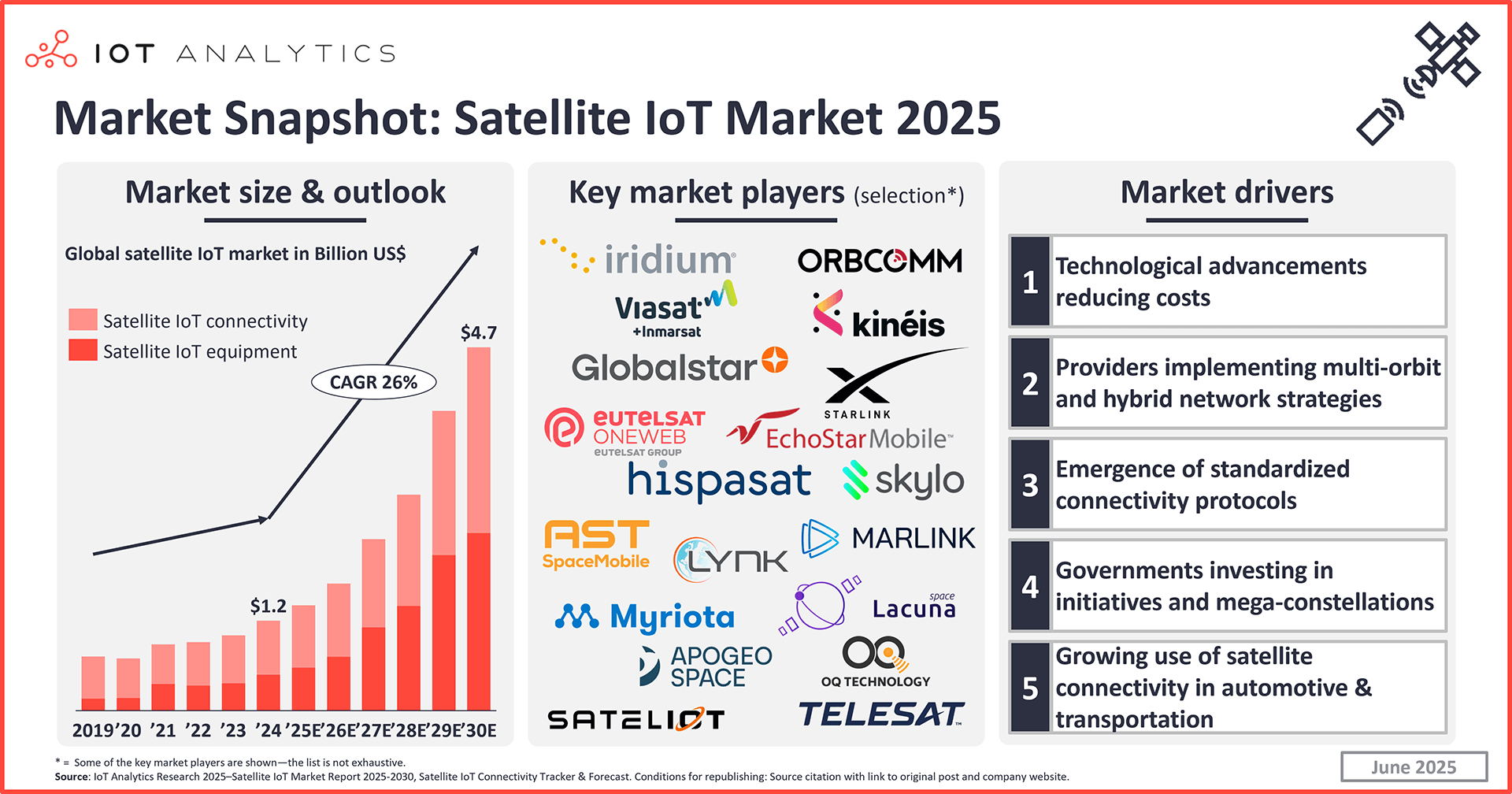
- The number of satellite IoT connections reached 7.5 million in 2024, according to IoT Analytics’ Satellite IoT Market Report 2025–2030 (published June 2025).
- The market for satellite IoT connectivity and equipment is expected to grow at a 26% CAGR until 2030, surpassing $4.7 billion.
- 5 key drivers are poised to propel this growth:
- 1) Technological advancements reducing costs
- 2) Providers implementing multi-orbit and hybrid network strategies
- 3) Emergence of standardized connectivity protocols
- 4) Governments investing in initiatives and mega-constellations
- 5) Growing use of satellite connectivity in the automotive and transportation industries
Why it matters
- For satellite IoT market players: The satellite IoT market is very dynamic, with new technologies and approaches disrupting legacy satellite operations. Vendors should invest in interoperability, hybrid networks, and standardized protocols to maintain competitive advantages and capture a wider range of IoT applications across industries.
- For satellite IoT adopters: Connectivity costs are declining, and new approaches are enhancing satellite latency and reliability. Adopters should explore satellite IoT as a viable solution for remote, underserved applications while staying updated on the emerging technology landscape to ensure scalability and cost efficiency in their deployments.
This article is based on insights and data from these reports and trackers:
Satellite IoT
Market Report
2025-2030
A 235-page report detailing the satellite IoT market, including market sizing with breakdowns & forecast, competitive landscape, key use cases, case studies, vendor profiles, trends, and more.
Satellite IoT Connectivity
Tracker & Forecast
A tracker and forecast covering global satellite IoT connectivity from 2019 to 2024, with projections through 2030. Includes data by company, region, connectivity mode, technology, industry, and more.
Already a subscriber? View your reports and trackers here →
Satellite IoT market overview and outlook
Satellite IoT connections surpass 7 million, with strong growth expected ahead. According to IoT Analytics’ 235-page Satellite IoT Market Report 2025–2030 (published June 2025), global satellite IoT connections reached 7.5 million in 2024. IoT Analytics forecasts strong growth in connections, propelling combined satellite network operator (SNO) and equipment vendor revenue growth at 26% CAGR until 2030, surpassing $4.7 billion.
Satellite IoT is experiencing a period of accelerated innovation, with a number of drivers setting the stage for the forecasted growth. Below are 5 key drivers based on the analysis in the report, based on its accompanying IoT satellite connectivity tracker and forecast database (updated in June 2025).
5 key satellite IoT market growth drivers through the end of the decade
1. Technological advancements reducing costs
The satellite industry is shifting from heavy geostationary (GEO) satellites to cost-efficient low earth orbit (LEO) miniaturization. Historically, legacy satellite operators prioritized launching large satellites—often exceeding 1,500 kg—into GEO orbit, where both manufacturing and launch costs are significantly influenced by payload weight and orbital altitude. However, there is a growing trend toward manufacturing and launching miniaturized satellites in LEO, and this has led to reduced connectivity costs as well.
Manufacturing costs
Standardized production and modular designs reduce satellite costs. Satellite manufacturers have adopted standardized mass production techniques, leading to significant cost reductions. For example, UK-based OneWeb manufactures 2 satellites per day, each weighing 147 kg. In addition to standardized manufacturing, vendors are increasingly using modular designs to produce satellite subsystems in large quantities, driving efficiency and scalability. Additionally, Spain-based FOSSA Systems offers a picosatellite, the FOSSASat-2, costing between €100k and €250k. This shift has been driven by technological advancements that enable the production of lightweight, cost-effective satellites with shorter development and deployment cycles. Further, the manufacturing cost of smaller satellites for IoT is less compared to heavy satellites primarily because of their simpler design, lower material, and mass production advantages.

Launch costs
Advancements in launching technology drive manageable costs. The cost of launching satellites has significantly decreased in recent years, primarily due to advancements by providers like US-based SpaceX. Its Falcon 9 offers launch services at less than $3,500/kg to LEO due to its reusable nature, making it more cost-effective compared to traditional satellite launch providers (for reference, the average cost to launch a satellite in 1995 was ~$50,000/kg). Launching a satellite into LEO is more cost-effective than GEO because LEO requires much less energy and fuel, resulting in lower launch costs per kilogram.
Connectivity costs
Satellite connectivity costs are falling due to smaller, scalable satellites. The reduction in connectivity costs is directly tied to these improvements in satellite manufacturing and launch economics. Smaller, standardized satellites deployed in LEO require less capital and can be launched more frequently, increasing the scalability of the network; thus, the subscription cost of satellite connectivity can be reduced further compared to the satellite connectivity from satellites in GEO orbit, lowering the cost per bit of data transmitted. SNOs are passing on these cost savings to their customers. Italy-based Apogeo Space, for example, provides free satellite connectivity for the first 5 IoT devices with up to 2 messages a day (10 bytes/message/device). This trend has surged interest in deploying IoT projects utilizing satellite connectivity across various industry verticals, as well as among consumers. Post-pandemic, the growing demand for outdoor recreational activities, coupled with the increased availability of tracking devices, has expanded the subscriber base by utilizing satellite connectivity.
2. Providers implementing multi-orbit and hybrid network strategies
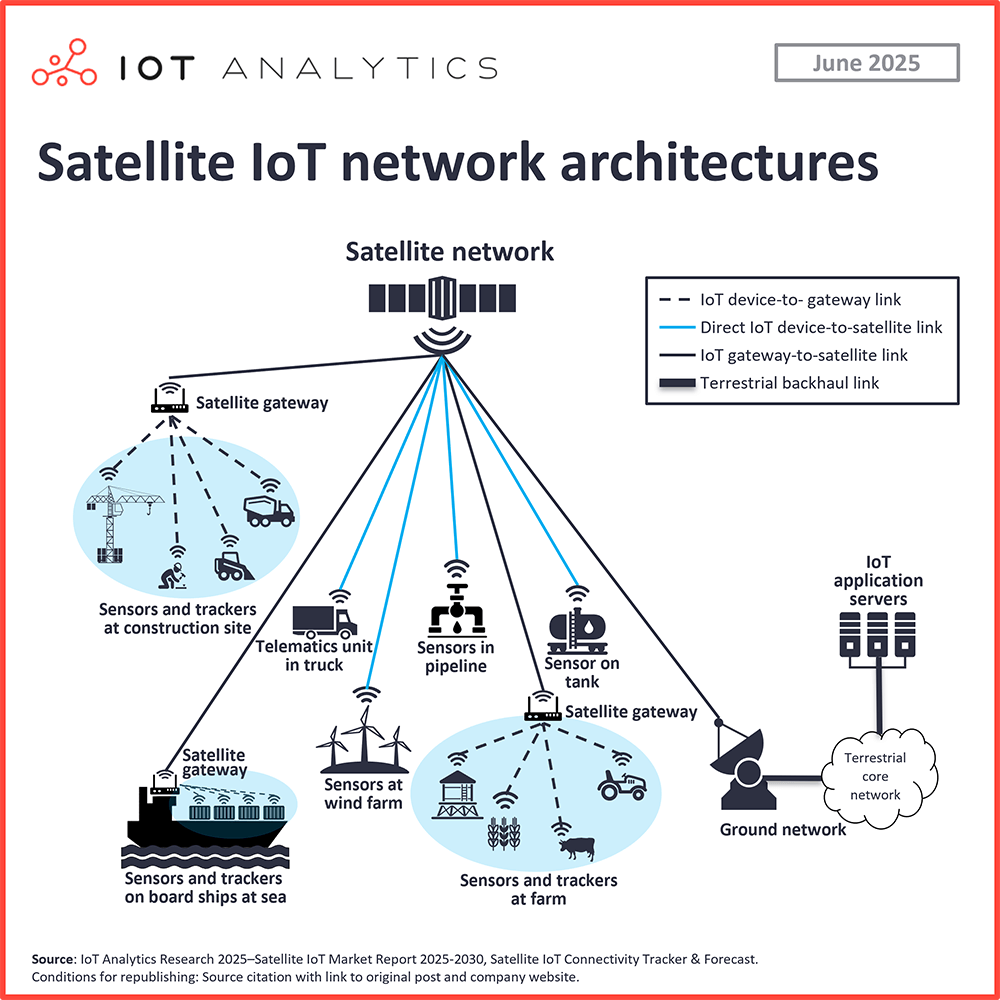
Legacy SNOs adjusting connectivity strategies to sustain market leadership. Legacy SNOs, such as US-based Viasat and Iridium, currently lead the satellite IoT market. In 2024, these companies held the highest share of satellite IoT connections—a position they are expected to maintain through 2030, despite a gradual decline in overall market share due to heavy competition from new market entrants. To sustain their dominance, these operators are not only expanding satellite capacity but also adopting new multi-orbit and hybrid connectivity strategies, leveraging their proprietary ecosystems to deliver more flexible, resilient services across diverse use cases. By expanding coverage and reducing latency through multi-orbit deployments, these operators can support a broader range of IoT applications—ultimately driving higher connection volumes across sectors.
Multi-orbit constellations
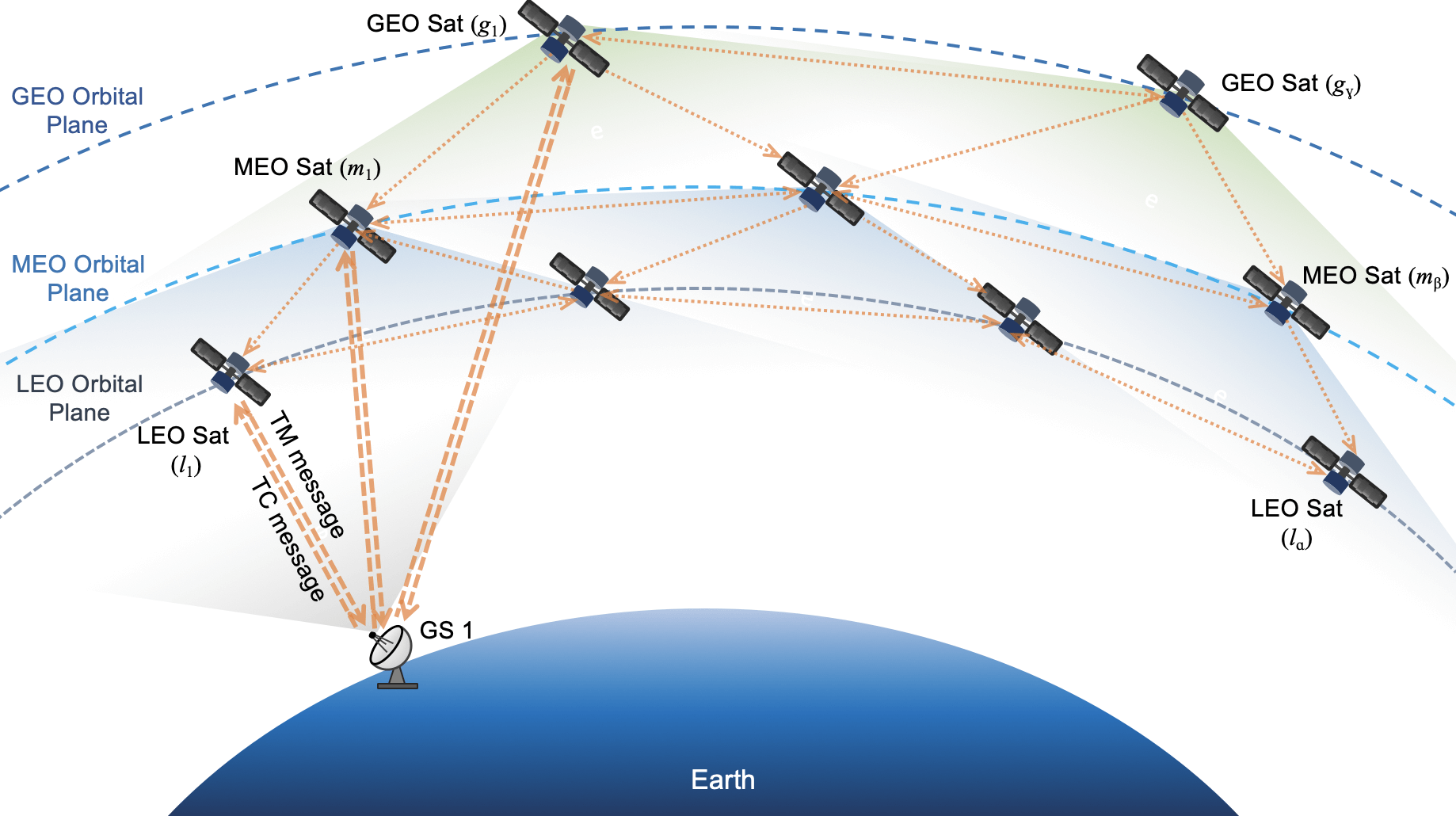
Multi-orbit strategies optimize satellite connectivity for IoT applications. SNOs are combining LEO, medium Earth orbit (MEO), and GEO constellations to optimize connectivity. Each orbit offers distinct advantages: LEO satellites provide low-latency communication, MEO satellites offer more coverage and slightly lower latency, while GEO satellites, despite their higher latency, provide continuous global coverage. By integrating satellites across these orbits, operators can ensure that their networks provide both global reach and the performance needed for diverse IoT applications, from asset tracking to real-time fleet management.
For example, in April 2024, Luxembourg-based SES announced its $3.1 billion acquisition of Intelsat, combining SES’s MEO O3b mPower system with Intelsat’s GEO satellite fleet to create a unified multi-orbit platform. Just prior, in March 2024, Intelsat committed $250 million over 6 years to partner with France-based Eutelsat on the development of the Next Generation OneWeb LEO constellation. Eutelsat had previously merged with UK-based OneWeb in September 2023, further strengthening its LEO–GEO integration.
Hybrid connectivity
Collaboration between mobile network operators (MNOs) and SNOs drives hybrid satellite-terrestrial connectivity. Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) have begun collaborating with SNOs to provide global coverage and hybrid connectivity using terrestrial cellular networks and non-terrestrial satellite networks. Recent industry developments highlight the growing momentum behind hybrid satellite-terrestrial connectivity, particularly using 3GPP-based standards and spectrum-sharing models.
In March 2024, US-based SNO Omnispace partnered with South Africa-based MNO MTN to integrate its non-terrestrial (NTN) network with MTN’s terrestrial infrastructure, using 3GPP standards to support both consumer mobile and enterprise IoT services. Similarly, Germany-based MNO Deutsche Telekom in February 2024 launched satellite-enabled IoT offerings through partnerships with US-based Intelsat and Skylo—introducing the “IoT Satellite Connect” tariffs for stationary use cases like wind and solar parks and the “IoT Business LPWA” tariff to support narrowband IoT devices via GEO satellites.
3. Emergence of standardized connectivity protocols
Legacy satellite module market share to significantly decline by 2030 as new standards rise. In 2024, legacy satellite connectivity module technology dominated with a 98% market share, but according to the report and its accompanying IoT satellite connectivity tracker and forecast database (updated in June 2025), this is forecast to fall to 49% by 2030. A key driver of this shift is the move toward open, device-compatible architectures such as 3GPP-based NTN and unlicensed technologies such as LoRa-based networks, which enable service expansion across diverse industry verticals. Standards like these are driving down device and integration costs while increasing interoperability across different network types and geographies.
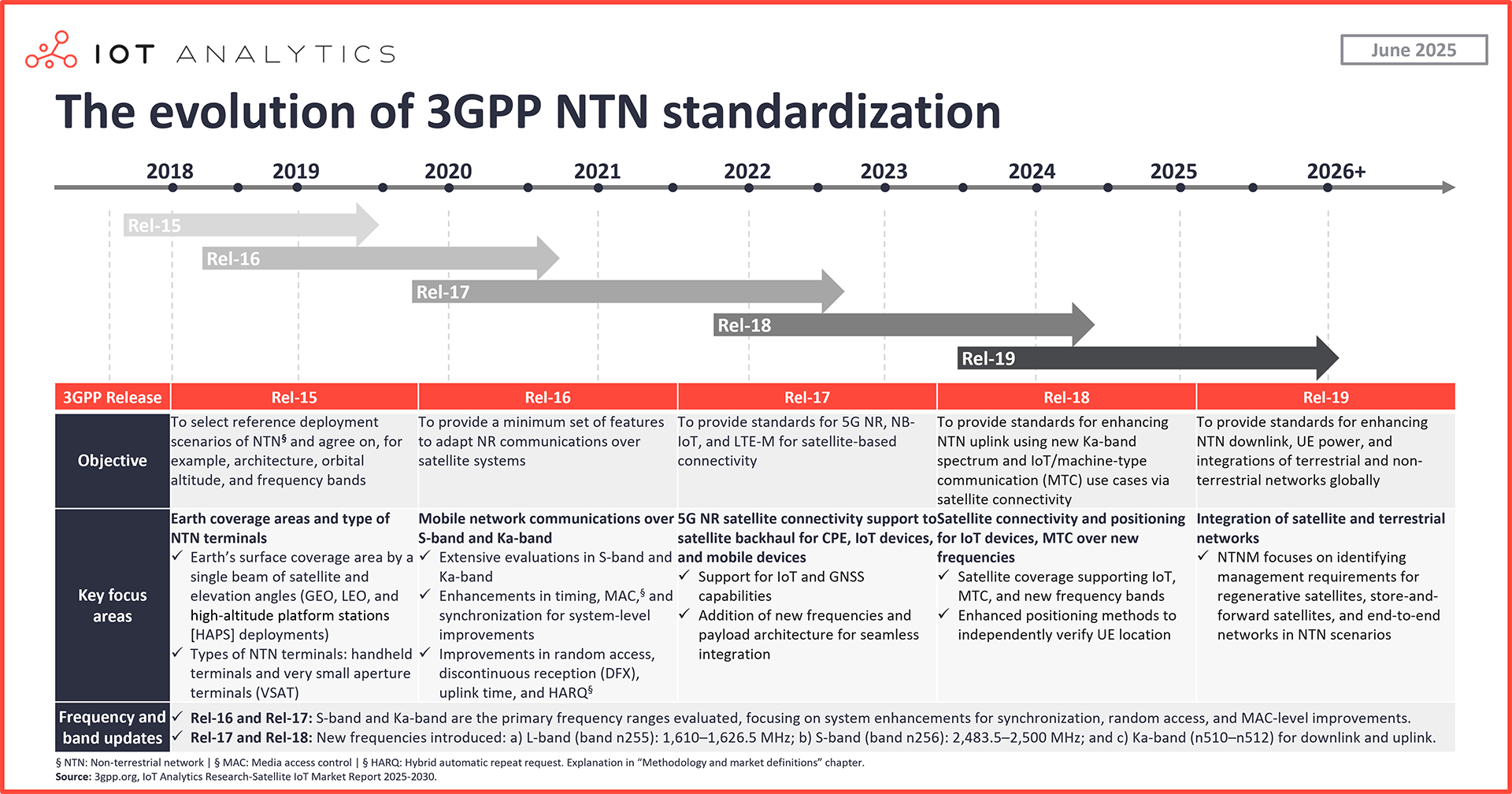
Overview of 3GPP NTN:
3GPP’s evolution of NTNs from Release 15 to Release 19 enables reliable, global connectivity beyond terrestrial infrastructure:
- Rel-16 adapted NR protocols for satellite use, ensuring stable communication over S- and Ka-band.
- Rel-17 introduced satellite-based backhaul specifically supporting IoT devices, enabling connectivity in rural, maritime, and industrial environments.
- Rel-18 enhanced uplink efficiency and positioning accuracy, which is critical for asset tracking, environmental monitoring, and smart agriculture.
- Rel-19 will advance full integration with terrestrial networks through regenerative and store-and-forward satellite capabilities.
Legacy satellite operators are adopting new standards to stay competitive. Legacy SNOs with established market dominance are increasingly adopting these new standards to keep pace with changing technology and the rising demand for accessible, standards-based IoT connectivity. Ireland-based EchoStar Mobile has launched a pan-European LoRa-enabled IoT network using GEO satellites to support low-power IoT applications. Additionally, US-based Iridium is also advancing its 3GPP-compliant NTN Direct service through Rel-19 integration and partnerships with chipmakers like Norway-based Nordic Semiconductor. These efforts reflect a broader shift by legacy players to expand their technology portfolios, increase connection volumes, and stay competitive in the evolving satellite IoT landscape.
IoT modules integrated with multiple connectivity options for flexibility. The IoT industry is evolving toward multi-radio, multi-band modules that integrate satellite, LoRa, cellular (e.g., LTE-M and NB-IoT), Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth to meet growing demands for flexible, reliable, and energy-efficient connectivity. For example, Taiwan-based IoT solutions provider REYAX’s RYLR924, launched in 2024, supports LoRa, Sigfox, and LR-FHSS across sub-GHz, 2.4GHz ISM, and 1.9–2.1GHz satellite bands. Meanwhile, Chinese module vendor SIMCom launched its SIM7070G-HP-S module in 2024. The module supports L- and S-band satellite frequencies along with cellular bands.
4. Governments investing in initiatives and mega-constellations
Governments are the primary drivers of satellite infrastructure demand. Governments are the largest early adopters and investors in satellite networks, driven by the need for secure, domestically built data transmission infrastructure. This sustained public sector demand is expected to accelerate growth in satellite connection volumes. In 2023, governments drove nearly 80% of global space infrastructure demand, led by the US and China’s defense and space programs. In Europe, over 70% of demand came from public sector buyers, with the European Space Agency (ESA) accounting for more than 40% of total sales.
In November 2024, the European Commission (EC) and ESA signed a contract with SpaceRISE to launch the Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity and Security by Satellite (IRIS²) initiative. The project involves building a network of 290 satellites in LEO and MEO by 2030 and is led by Eutelsat, Spain-based Hispasat, and SES, with support from the EC, EU member states, and the ESA. The total cost for the 12-year contract is €10.6 billion, funded jointly by the EU (€6 billion over 3 financial years), the ESA (€550 million), and the private sector (€4 billion). The goal is to secure communications for government operations, focusing on border and maritime surveillance, crisis management, safe internet access for citizens, and protecting EU embassy communication channels while also enhancing defense capabilities.
Additionally, in November 2023, China launched an initiative to enhance its commercial space ecosystem, focusing on satellites, vehicles, and related infrastructure. The Chinese government is financially supporting 2 mega-constellations to strengthen its presence in LEO and establish dominance in global satellite connectivity: Guowang and Qinfan.
Guowang (or GW-National Network) aims to establish a constellation of approximately 13,000 satellites. The first 10 launched on December 16, 2024, under the management of China Satellite Network Group, a state-owned enterprise. Though the total number of satellites is not publicly known, China has had 33 orbital attempts to date, with the last set in early June 2025. Meanwhile, the Qianfan (or Thousand Sails/G60 Starlink) project plans to deploy 14,000 satellites, with the first 18 launched on August 7, 2024. Shanghai Spacecom Satellite Technology (or SSST) raised $6.7 billion yuan ($943 million) in funding for the constellation, backed by venture capital firms under the Shanghai Municipal Government and CAS.
5. Growing use of satellite connectivity in the automotive and transportation industries
Transportation and logistics likely to dominate 3GPP NTN connectivity usage. The transportation and logistics sector is expected to account for 60% of the total share of upcoming 3GPP NTN IoT connectivity, driven by key applications that enhance safety, efficiency, and operational continuity. These include emergency assistance and roadside alert services in areas without terrestrial coverage, continuous fleet tracking and telematics for real-time monitoring, and over-the-air software updates to maintain vehicle performance and security across global routes.
Viasat has demonstrated D2D satellite connectivity for the automotive sector. Conducted in southern Brazil, the trials enabled vehicles to connect directly to Viasat’s L-band satellites via Skylo’s network using 3GPP NTN-compliant modules from China-based connectivity module manufacturer Quectel. The system allowed seamless switching between satellite and cellular networks, ensuring uninterrupted coverage in remote areas.
Further, during a recent 5G Automotive Association event in Paris 2025, Luxembourg-based cellular network access device supplier Rolling Wireless showcased its RN941Y module, which supports multiple NB-NTN bands based on 3GPP Release 17. In a joint demonstration with US-based transportation equipment manufacturer Cubic, Netherlands-based automotive company Stellantis, France-based energy and mobility innovation solutions institute Vedecom, and Viasat, Rolling Wireless highlighted how satellite connectivity can extend automotive coverage and enhance vehicle safety. The demonstration illustrated 2 key use cases:
- Emergency alerts via NTN: Vehicles were shown transmitting emergency alerts through NTN, enabling access to emergency services even in areas with limited terrestrial coverage.
- Weather alert broadcasts: Backend servers pushed region-specific weather warnings to connected vehicles, enabling early awareness of hazardous driving conditions.

Analyst takeaway: Key opportunities and challenges in the satellite IoT market
Satellite IoT is crucial in remote, underserved sectors. As detailed in the Satellite IoT Market Report 2025–2030, satellite IoT connectivity delivers true value not just as a backup or complement to terrestrial networks but in verticals where terrestrial coverage is limited or non-existent as well. The most meaningful use cases—such as asset tracking in logistics, environmental monitoring, agriculture, maritime, and energy—are located in remote, underserved regions. These remain the core focus areas where satellite IoT is not just relevant, but essential.
The satellite IoT ecosystem is moving from single to diverse technology. The satellite IoT market is undergoing a significant transformation, shifting from reliance on single, proprietary connectivity solutions toward a more diverse and interoperable technological ecosystem. Emerging technologies such as LoRa, Mioty, and 3GPP-based NTN are gaining traction, enabling standardized, open architectures that support a broader range of use cases. Additionally, innovative developments like Bluetooth-from-space are expanding the scope of low-power, short-range satellite communication. This diversification reflects a broader industry movement toward hybrid, multi-network solutions capable of addressing the demand for global IoT connectivity.
Standardized 3GPP satellite IoT connectivity will remain limited until the commercial model is finalized. The immediate commercial returns for satellite operators will largely come from consumer mobile markets. In contrast, the share of standardized 3GPP satellite connectivity within the IoT segment is expected to remain a small fraction of the overall market in the near term. Key commercial questions—such as pricing structures and revenue-sharing models between satellite operators and mobile network operators—are unresolved, making mass-scale momentum delayed until after 2026.
Mega constellations challenge traditional satellite operators’ profitability and competitiveness. Mega constellations from companies like Starlink and US-based Amazon Kuiper present a major challenge for other IoT satellite operators. These tech giants have the financial muscle to fully fund and deploy their satellite constellations on a scale, giving them a clear advantage in terms of reach, speed, and service affordability. Important to note that neither company currently plays in the direct-to-device IoT satellite market but that Starlink has previewed market entry into IoT later in 2025, according to the Starlink website. Meanwhile, many traditional operators face a difficult cycle—managing the high capital expenditure required for satellite deployment, attempting to monetize only a portion of the constellation in service, and relying on that limited revenue to raise funds for future launches. For these operators, profitability remains a long-term uncertainty, with sustained competitiveness dependent on strategic pivots and potential partnerships.
Point in case: Between May 2024 and May 2025, Starlink launched 600+ direct-to-cell satellites, highlighting its rapid expansion. In contrast, Switzerland-based Astrocast—recently delisted from Oslo’s Euronext Growth—struggles to scale its 18-satellite LEO constellation amid tight funding and limited investor access.
Disclosure
Companies mentioned in this article—along with their products—are used as examples to showcase market developments. No company paid or received preferential treatment in this article, and it is at the discretion of the analyst to select which examples are used. IoT Analytics makes efforts to vary the companies and products mentioned to help shine attention to the numerous IoT and related technology market players.
It is worth noting that IoT Analytics may have commercial relationships with some companies mentioned in its articles, as some companies license IoT Analytics market research. However, for confidentiality, IoT Analytics cannot disclose individual relationships. Please contact compliance@iot-analytics.com for any questions or concerns on this front.
More information and further reading
Are you interested in learning more about the satellite IoT market?
Satellite IoT
Market Report
2025-2030
A 235-page report detailing the satellite IoT market, including market sizing with breakdowns & forecast, competitive landscape, key use cases, case studies, vendor profiles, trends, and more.

Satellite IoT Connectivity
Tracker & Forecast
A tracker and forecast covering global satellite IoT connectivity from 2019 to 2024, with projections through 2030. Includes data by company, region, connectivity mode, technology, industry, and more.

Already a subscriber? View your reports and trackers here →
Related dashboard and trackers
You may also be interested in the following dashboards and trackers:
- Global Cellular IoT Connectivity Tracker & Forecast
- Global Cellular IoT Module and Chipset Market Tracker & Forecast
Related publications
You may also be interested in the following reports:
- IoT Asset Tracking & Visibility Adoption Report 2025
- Mobile World Congress and Embedded World 2025—Analyst Takeaways
- IoT Use Case Adoption Report 2024
Related articles
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- The evolution of enterprise IoT asset tracking: From locating assets to optimizing operations
- Winning in the asset tracking market: 5 lessons from adopters
- The top 10 IoT use cases
Subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter to stay up-to-date on the latest trends shaping the IoT markets. For complete enterprise IoT coverage with access to all of IoT Analytics’ paid content & reports including dedicated analyst time check out Enterprise subscription.

