Industrial IoT Market Reports
-

Equipment as a Service Market Report 2024–2028
From $3,000.00 -

IoT Commercialization & Business Model Adoption Report 2024
From $3,000.00 -

Industrial IoT & Industry 4.0 Case Study Report 2023
From $2,000.00 -

Predictive Maintenance & Asset Performance Market Report 2023–2028
From $3,000.00 -

Enterprise Augmented/Mixed Reality Market Report 2022–2027
From $3,000.00
Latest Insights: Industrial IoT
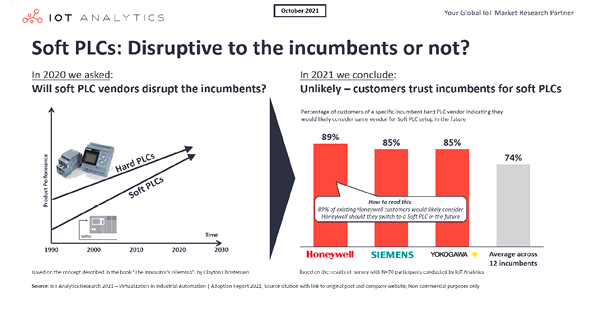
Soft PLCs: Revisiting the industrial innovator’s dilemma
In short Software based PLCs (programmable logic controllers) may pose an innovator’s dilemma to the incumbents of the industrial automation world and threaten their hard-PLC business.Our most recent research on the topic shows that the threat of disruption for incumbent vendors is lower than previously assumed because customers are indicating that they would stick to existing vendors for...
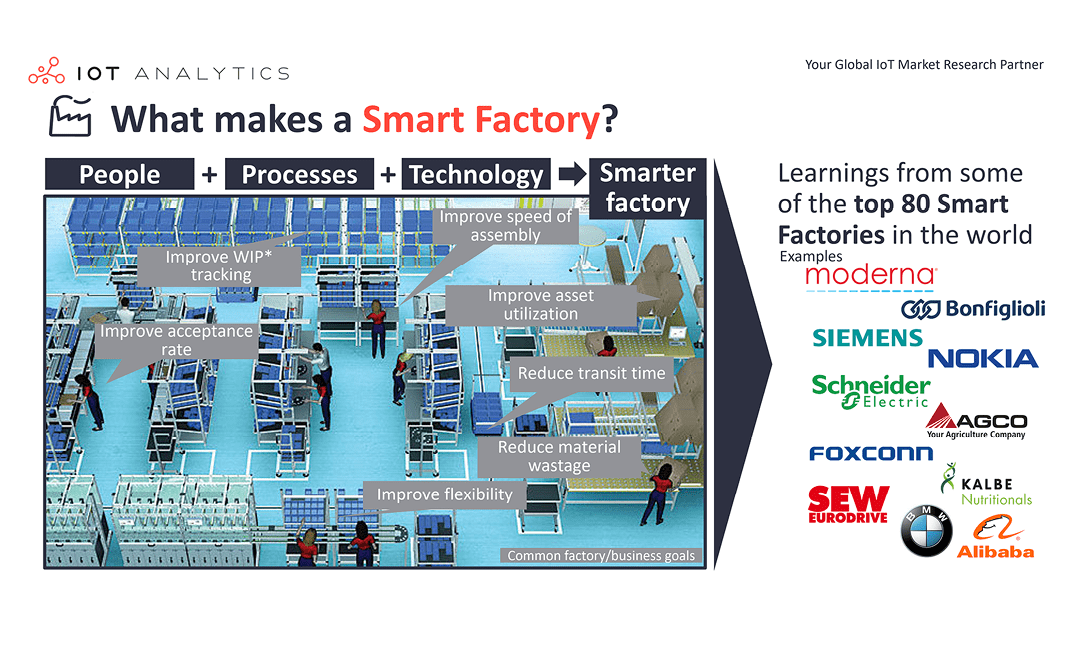
What are smart factories? 7 misconceptions and a definition
Key Insights Factories are becoming more intelligent, flexible, and sustainable through the power of technology, data, and the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT Analytics researched how 80 of the world’s best factories became so smart and discovered that, among other things, there is much more to smart factories than technology. Download report sample Why it matters? Customer demands are pushing...
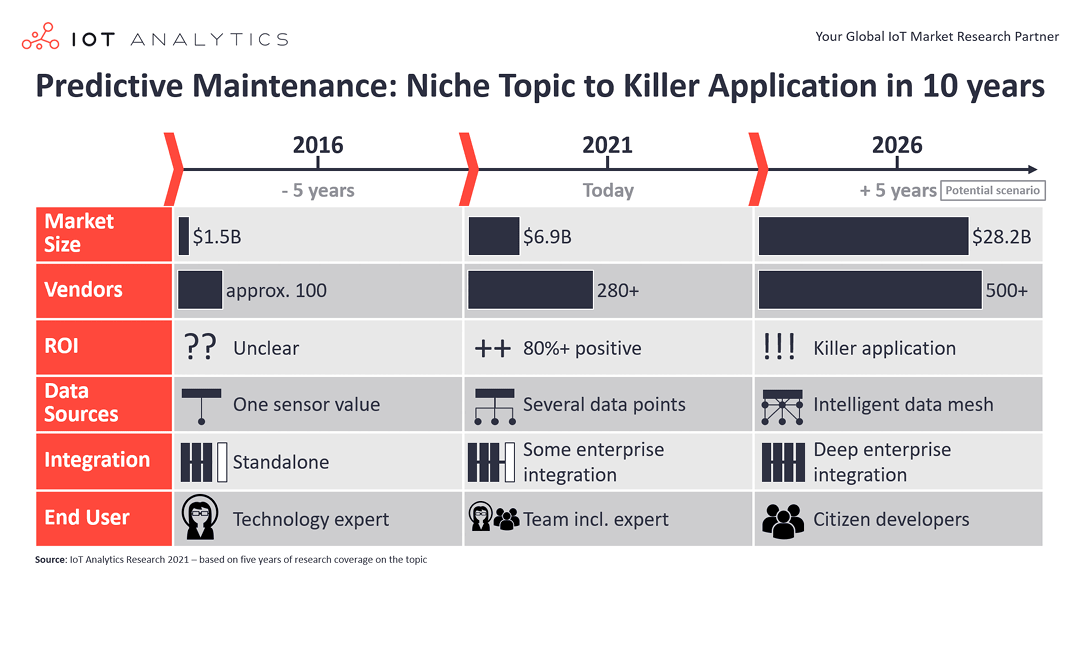
Predictive Maintenance Market: The Evolution from Niche Topic to High ROI Application
In short In just five years, predictive maintenance has moved from an uncertain, standalone niche use case to a fast-growing, high return on investment (ROI) application that is truly delivering value to users. These developments are an indication of the power of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), and the market is still in its infancy. A new IoT Analytics report...
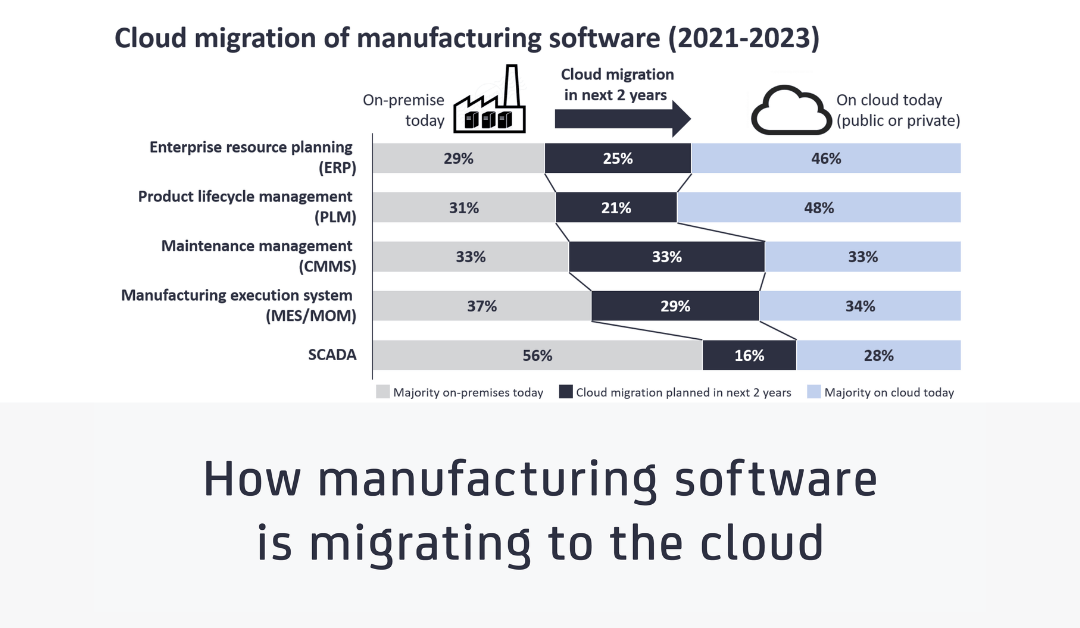
Cloud MES: How manufacturing software is migrating to the cloud
In short Enterprise software, such as ERP, is increasingly moving to the cloud; Cloud adoption for manufacturing software, such as MES/MOM, is much lower but accelerating. 29% of manufacturers in a recent survey indicated a move of MES software to the cloud in the next 2 years. The Cloud MES market is estimated to reach $2.34 billion by 2026. Why it matters? Offering cloud-based MES solutions...
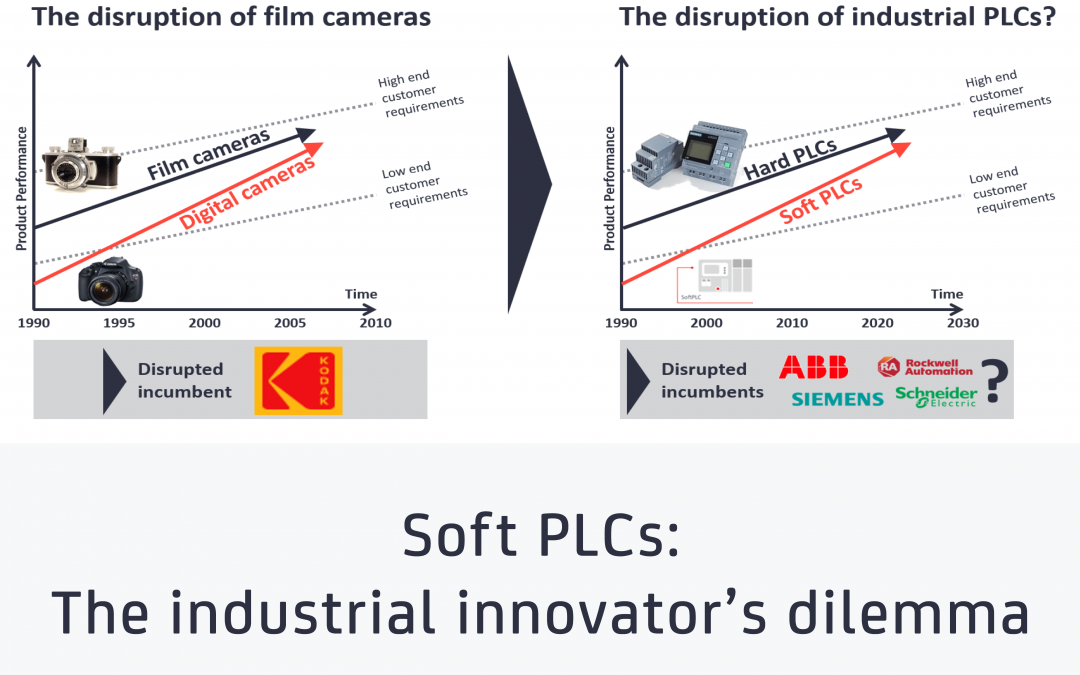
Soft PLCs: The industrial innovator’s dilemma
Update October 2021: IoT Analytics published a more recent blog on: Soft PLCs: Revisiting the industrial innovator’s dilemma. In short Software is increasingly replacing hardware in industrial environmentsSoftware-based controllers (Soft PLCs) today are reliable, powerful and flexible.Soft PLC adoption is expected to double between 2019 and 2025, posing an “innovator’s dilemma” for incumbent...
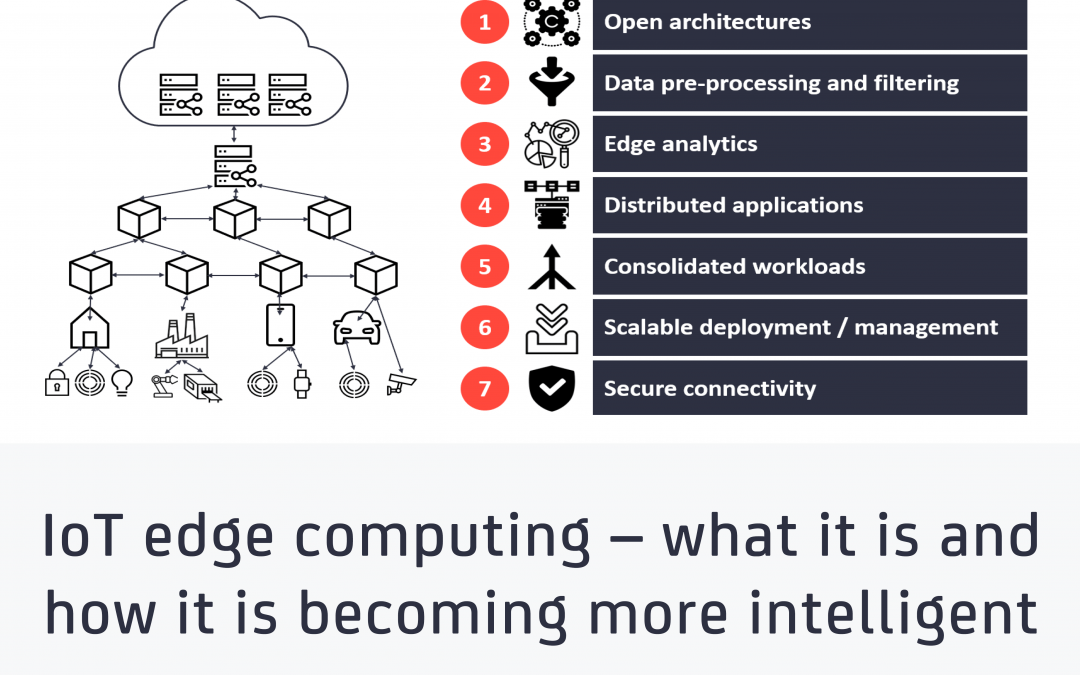
IoT edge computing – what it is and how it is becoming more intelligent
In short IoT edge computing resources are becoming increasingly intelligentThere are 7 key characteristics that make modern edge computing more intelligent (including open architectures, data pre-processing, distributed applications)The intelligent industrial edge computing market is estimated to reach $30.8B by 2025, up from $11.6B in 2020 (see new 248-page report) Why it matters IT/OT...
Insights By Category
Our View On Industrial IoT
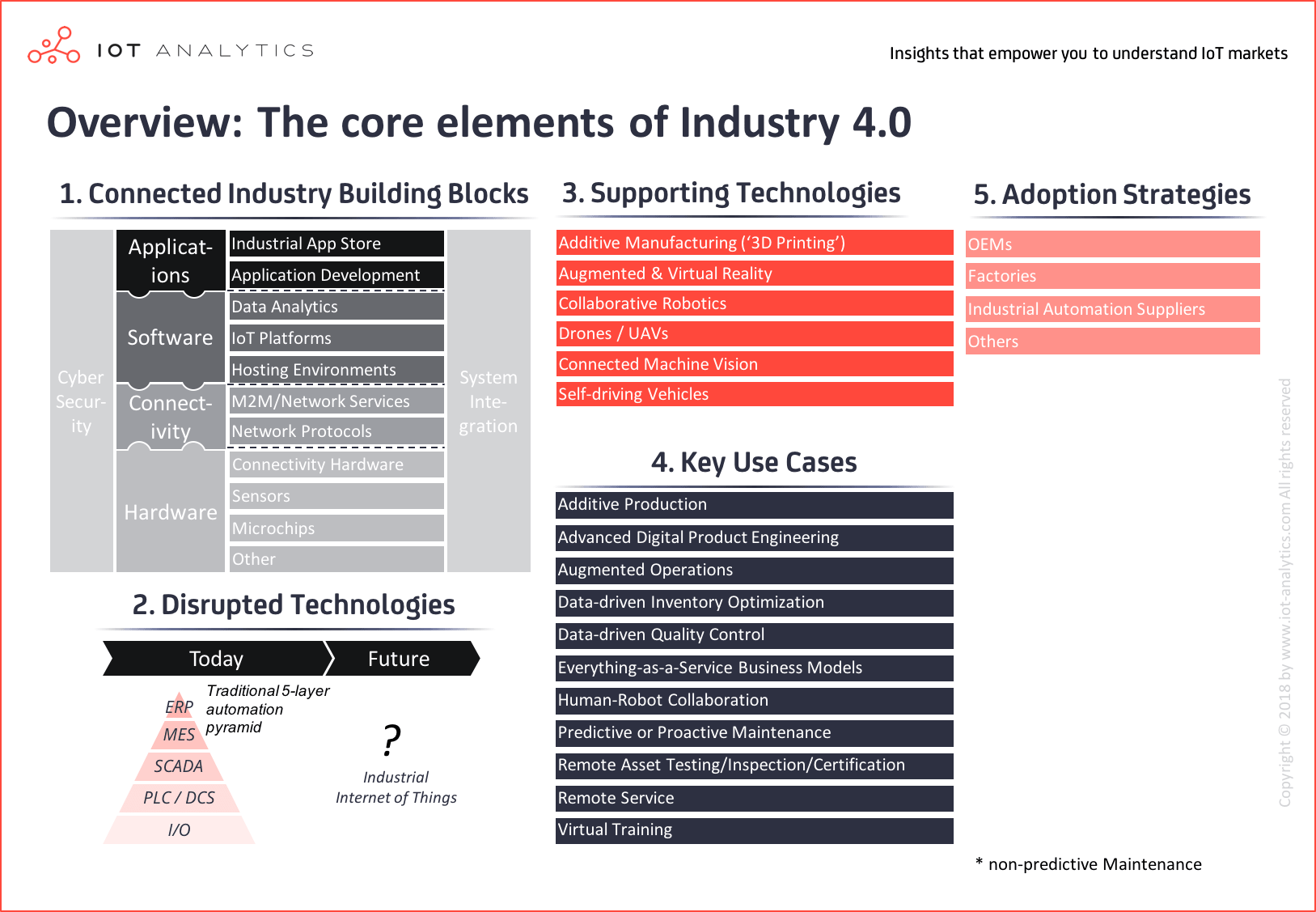
The industrial IoT research stream covers the core elements:
1. Connected Industry Building Block
- Hardware, such as chips, sensors or gateways
- Connectivity protocols and services
- Hosting environments, IoT platforms, and data analytics & AI
- Applications that are built on top of the software layer
- Cyber security technologies and methods used throughout the stack
- Systems integration, connecting systems both vertically and horizontally
2. Disruptive Trends
The technologies and standards which are being be altered or replaced by disruptive trends caused by I4.0 technologies.
3. Supporting Technologies
Six technologies frequently deployed alongside the connected industry building blocks to support the I4.0 key use cases.
- Additive Manufacturing (AM)
- Augmented and Virtual Reality
- Collaborative Robotics
- Connected Machine Vision
- Drones/UAVs
- Self-Driving Vehicles
4. Key Use Cases
Use cases implementing connected industry and/or supporting technologies.
5. Adoption Strategies
OEMs, factories, and industrial automation suppliers are all leveraging I4.0 technologies to differentiate themselves in the market.
Our Insights Are Trusted By















What Others Say About Us
“The Predictive Maintenance Study has served us very well! It was the catalyst that triggered the right internal discussions we should lead.”
“I find it really impressive how the IoT Analytics team have built up a broad and proprietary knowledge base around the Internet of Things and Industry 4.0 ecosystems.”
“I have now read the complete report and wanted to tell you that I find it extremely well done.”
Stay Up-to-Date With The Latest News & Updates
Access Premium Content
Gain access to our complete pool of insights and intelligence with a research subscription.
Join Our Newsletter
Be the first to know when we publish new insights and content.
Follow Us
Connect with us to gain access to exclusive updates from our team.