In short
- ChatGPT has sparked interest in generative AI applications in nearly every industry.
- According to new research from IoT Analytics, most generative AI applications are at a very early stage, with IoT-related use cases currently not in focus.
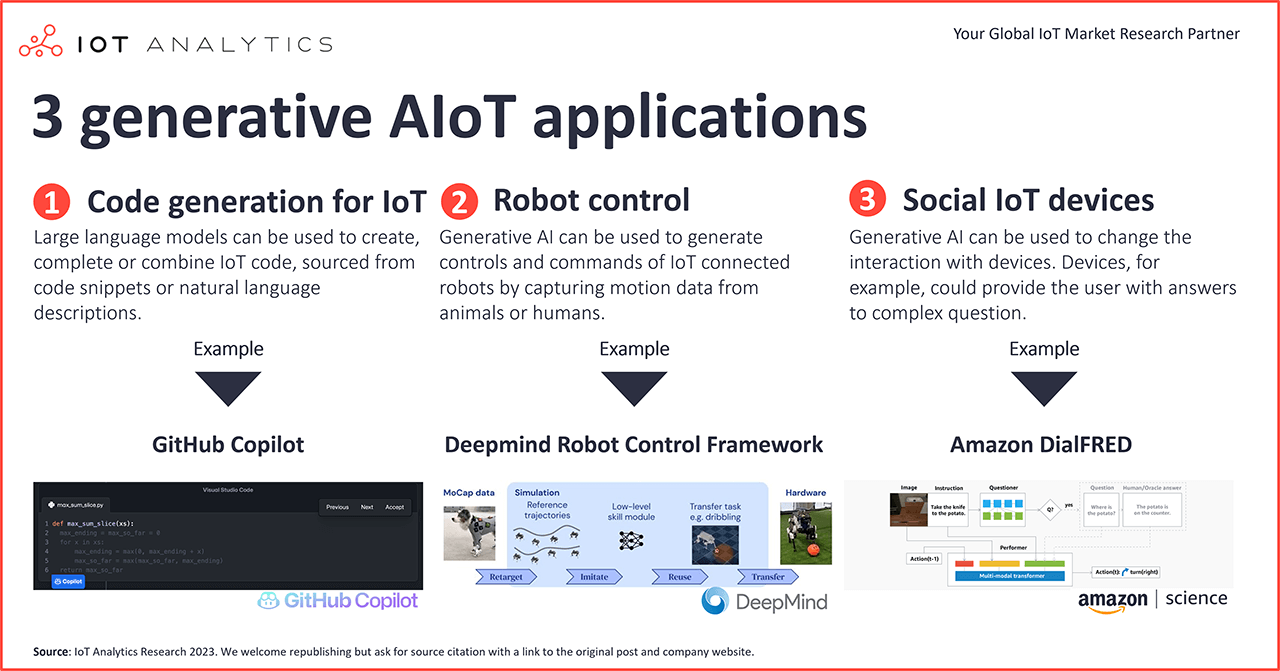
- Code generation for IoT, robotics control, and social IoT devices are some of the most promising IoT-related applications of generative AI.
Why it matters
- Generative AI and large language models are receiving serious attention right now.
- The IoT community is yet to produce a compelling combination of generative AI and IoT. Whoever comes up with the first convincing application may generate a first-mover advantage.
ChatGPT and generative AI
OpenAI released ChatGPT on 30 November 2022. The chatbot, which is built on the large language model GPT3 (GPT stands for general pretrained transformers), went viral and set records for the fastest growing consumer application in history, reaching 100 million active users within two months of its launch.
Surprising to many, the technology behind ChatGPT is not new. The base for it all, the transformer architecture, is centered on a 2017 Google research paper titled “Attention Is All You Need.” As of early March 2023, the paper was cited more than 67,000 times and can be seen as the source of generative AI innovation. The first GPT by OpenAI and Alphabet’s BERT language models were published in 2018. Amazon, Meta, IBM, Alibaba, and Tencent subsequently all published their own large language models.
So why did OpenAI’s ChatGPT become so popular when it is neither new nor unique?
The answer comes down to ChatGPT’s ease of use and accessibility, as it was the first state-of-the-art large language model made available for free to everyone with internet access.
What are the key use cases that generative AI enables?
As a market research company looking at IoT and IoT-related topics, we at IoT Analytics felt compelled to understand the impact generative AI can have on connected devices, typical IoT use cases, and IoT technology in general. We published our findings in the Generative AI Trend Report. The report discusses the technology in general, looks at the competitive landscape, and then dives into use cases of generative AI related to IoT scenarios. Here are 3 of the 9 use cases we identified at the intersection of generative AI and IoT:
3 Generative AI Applications for IoT

Application #1: Code generation for IoT
Large language models can be used to create, complete, or combine software code, whether sourced from code snippets or natural language descriptions, and can be applied to various domains, tasks, and programming languages. With such capabilities, these models can aid both professional and amateur developers in constructing innovative applications. Generative AI is already available in many IDEs. Although already used by software developers, many emphasize that generative AI is not likely to replace developers anytime soon. We should think of it as another tool in the toolbox for code generation, similar to no-code/low-code tools being added to the general software development toolbox in recent years.
Example:
GitHub Copilot is a new cloud-based AI tool that uses OpenAI’s Codex model to suggest software code and entire functions in real time. Users receive suggestions from GitHub Copilot either by starting to write the code or by writing a natural language comment describing what they want the code to do. GitHub Copilot analyzes the context in the file the user is editing and related files and offers suggestions from within the text editor. GitHub Copilot can be used for many types of software code deployed for IoT-centric applications or on IoT devices. It can be integrated into several IDEs such as Microsoft’s VS Code or Jetbrain’s Pycharm.
Practitioners’ opinion:
“I had a specific IoT program idea for something I wanted to build in Node-RED, and I tried to have ChatGPT build it for me. It was able to generate the code that got me 80% of the way there, but ultimately I ended up needing a good developer to help me think through a couple of details that would have been difficult/time consuming to work through with ChatGPT.”
“I do not think generative AI will replace the need for good developers that understand what the best way to do things are to solve specific problems, but it may replace average developers that simply build exactly what they are told without thinking about the problem the code is trying to solve.”
Product manager of edge solutions at an industrial automation company
Application #2: Robot control
Generative AI could have an impact on how autonomous (IoT) devices are controlled, e.g., robots. By capturing motion data from animals or humans, generative AI can be used to generate control logic and commands for robots. Instead of deterministically programming movements for each leg of a robot dog, for example, generative AI models can be utilized to generate the movements of individual parts and make the robot dog walk complicated, interconnected steps. Moreover, generative AI models can help robots make sense of their surroundings and connect so-called horizon goals with more intermediate steps to reach the goals (e.g., fill a glass with juice). Robots can then generate intermediate tasks without the need for human interventions that are necessary to reach the higher horizon task (e.g., open the fridge first and find a glass).
Example:
In August 2022, Alphabet’s Deepmind showcased a framework that enables robots to move and perform tasks more “naturally” by learning from human or animal movements. Developing the ability to manipulate objects through robotic arms presents a difficult control challenge, but enhancing robot movements to appear more lifelike carries numerous advantages. For example, it is essential to establish stable and consistent behavior when traversing uneven terrain or handling delicate items. Inconsistent movements can result in damage to the robot or its surroundings and deplete its power source. As a result, considerable resources are frequently allocated to designing learning goals that enable robots to perform specific tasks safely and efficiently.
Application #3: Social IoT devices
Today’s IoT connected devices allow users to access data via some form of API. Usually, these offer predestined sets of information, e.g., usage, battery, and asset health. Generative AI, however, could be used to make device communication “more social” in three ways:
- Allowing the device to answer complex questions a user may have.
- Allowing the end user to talk to the device to change settings.
- Allowing the devices themselves to use generative AI to generate answers. The example below shows how a large language model can be used to guide a robot after it has been given unclear instructions and is stuck.
Example:
Amazon has developed the DialFRED framework, which allows robots to ask questions if they are unsure. Through reinforcement learning, the questioner model is fine-tuned to ask the right types of questions at the right time to benefit task completion. The framework includes an ”oracle” that automatically produces answers to the generated questions, using ground-truth metadata from the simulation environment. DialFRED thus provides an interactive Q&A framework for training embodied dialogue agents.
Practitioners’ opinion:
“I would expect to see, in the near future, the generative AI in IoT products to work as personal assistant of the users, learning their preferences, giving them recommendations [and] ideas—in different formats—and making it easier for people to have a dialogue with their smart products and use technology.”
IoT go-to-market strategist at a large IT company
Our Take
The Generative AI Trend Report identifies a number of generative AI models and their applications, but only few models focus on IoT. It is important to note that the flood of recent news and blogposts could create the feeling that generative AI is already a majorly adopted technology across many industries. The reality is different, especially for IoT in 2023.
With the exception of some prominent examples, such as Salesforce EinsteinGPT or GitHub Copilot, most projects that focus on the use of generative AI applications are limited to the PoC stage or are even theoretical research papers. IoT applications are particularly far away from being rolled out on a large scale. In addition, most generative AI models today mainly focus on text and images, and only a limited number of models are focused on sensor data as an input. Moreover, the accuracy of generative AI solutions in IoT settings must usually be very high. A “most likely” answer is often not good enough, and the result often needs to be available quickly, e.g., in the case of a connected car that needs an immediate decision on what action to take.
Our research suggests that the existing generative AI landscape is not focused on IoT data at all (except for image data). The popular models that are released and tested by OpenAI, Google, DeepMind, Meta, or Tencent are mainly focused on creating texts, images, or sounds. Therefore, the Generative AI Trend Report shows a limited number of IoT applications so far, and there are none for ChatGPT specifically.
Make no mistake, however, that such models can be part of an IoT setup, such as so-called “social IoT devices.” We believe that there may be an opportunity here: The first IoT-focused vendors to utilize generative AI at scale may generate a first-mover advantage.
Practitioner’s opinion:
“We do work a lot with AI/ML, but to be honest, very few of the IoT applications we have integrated so far use AI. For example, none of the production sites that we have helped use true AI/ML, apart from some prototypes. The potential for analyzing images, text, [and] sound using generative AI is great, but generative AI adoption so far: none.”
Executive at IoT system integrator in Sweden
Are you interested in learning more about generative AIoT applications?
IoT Analytics is a leading global provider of market insights and strategic business intelligence for the Internet of Things (IoT), AI, Cloud, Edge, and Industry 4.0.
Generative AI Trend Report
A 36-page report highlighting the state of generative AI models including technology overview, competitive landscape, trends & challenges, and an IoT deep-dive including case studies and potential use cases
Related publications
You may be interested in the following publications:
- Machine Vision Market Report 2022-2027
- Industrial AI and AIoT Market Report 2021–2026
- Industrial AI Software Platform Vendor Landscape Report 2021
- Predictive Maintenance Market Report 2021-2026
Related articles
You may also be interested in the following recent articles:
- Top 7 upcoming machine vision applications—enabled by recent advances in AI, cameras, and chips
- The rise of industrial AI and AIoT: 4 trends driving technology adoption
- Predictive Maintenance Market: The Evolution from Niche Topic to High ROI Application
Related market data
You may be interested in the following IoT market data products:
Global IoT Enterprise Spending Dashboard
Are you interested in continued IoT coverage and updates?
Subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter to stay up-to-date on the latest trends shaping the IoT markets. For complete enterprise IoT coverage with access to all of IoT Analytics’ paid content & reports including dedicated analyst time check out Enterprise subscription.


