In short
- Some of the latest IoT chipset and edge trends were on full display at the 2023 Embedded World Exhibition & Conference (in March 2023).
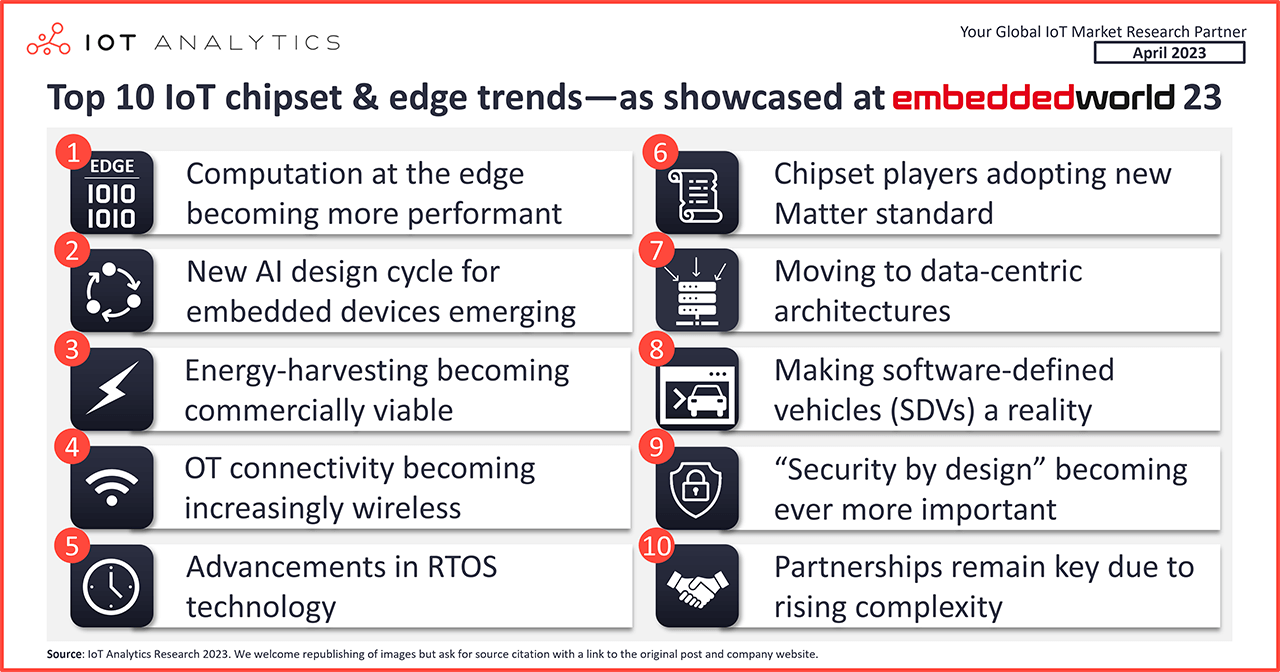
- As part of the Embedded World 2023 conference report, our team identified 19 industry trends related to IoT chipsets and edge computing, 10 of which are highlighted in this article.
Why it matters
- Embedded World is one of the world’s most important fairs for embedded systems. Technologies showcased in the fair are widely applicable to any company dealing with computerized hardware or the Internet of Things.
About Embedded World 2023
Embedded World, a leading event for the embedded systems community, was back in action a few weeks ago. The event that took place from 14 March to 16 March 2023 in Nürnberg, Germany, showcased, once again the latest developments and innovations in embedded systems, embedded software, chipsets, edge computing and related topics.
Attendance, although up 55% from the previous year, fell slightly short of reaching pre-pandemic participation levels, with a 16% decrease compared to 2020 (27,000 visitors in total).
IoT Analytics had a team of three analysts on the ground. They visited approximately 75 booths and conducted over 50 individual interviews with the aim of obtaining a comprehensive understanding of the most recent developments in embedded systems with a special focus on IoT.
This article highlights some of the major takeaways; our research clients can refer to the 35-page “Embedded World 2023—the latest IoT chipset and edge trends” event report for an in-depth discussion of the latest trends with examples and important quotes from the exhibitors.
10 IoT chipset and edge trends visible at Embedded World 2023
1. Computation at the edge is becoming more performant
As the complexity of IoT solutions increases, achieving faster response times while reducing overall latency becomes a key concern. To address this challenge, there is a growing trend toward integrating edge equipment with processors that offer higher computing power. At the fair, motherboard manufacturer Asrock, for example, showcased three state-of-the-art edge devices: 1. Its Edge AIoT hardware platform, iEPF-9020S-EY4/iEP-9020E Series, based on Intel’s 13th-Gen Core Processor (Raptor Lake-S). 2. Its Industrial IoT controller, iEP-7020E, based on the Intel Core i5-1350P processors (Raptor Lake-P). 3. Its edge controller/gateway, iEP-5000G, based on the Intel Atom x6000E processor. According to Intel, its 13th-generation processors improve multi-treaded performance by 41% compared to generation 12. The new Intel Atom processor is marketed to improve graphics performance by two times compared to the previous generation, among other advances.
2. A new AI design cycle for embedded devices is emerging
The embedded community is getting ready for hardware and devices supporting AI/ML execution at the edge. This means massive hardware design changes and complexity and an increased software stack complexity. AI hardware development company BrainChip showcased its new Akida AI processor IP that integrates with Arm’s new Cortex-M85 for handling advanced machine learning workloads at the edge. Chipmaker Renesas is one of the clients of Akida AI that showcased AI running on Arm Cortex-M85. AI-based machine vision applications are one of the driving forces of AI adoption at this point. Adlink Technologies and Vision Components, for example, showcased their respective new AI camera solutions that are capable of deploying large AI algorithms on their equipment.
3. Energy-harvesting is becoming commercially viable
Energy-harvesting technology promises to completely power or significantly extend battery life of low-power devices. The CTO of SiLabs at his keynote highlighted that he sees the energy harvesting technology “starting to get to a cost point where it makes economical sense.” A number of companies showcased energy harvesting solutions. Semiconductor company Nexperia designed a new power-management IC called NEH2000BY that allow for harvesting of ambient light or vibrations under changing conditions. Murata, Deutsche Telekom, and Nexperia showcased a new autonomous NB-IoT module that harnesses power from ambient light. The solutions are based on solar cells and the PMIC with MPPT feature.
4. OT connectivity is becoming increasingly wireless
Two years after the introduction of wireless I/O link, the technology seems to have been implemented in many real-world deployments, notably in the machinery sector. One of the key advantages of wireless technology is better space utilization. However, there is still a long way to go. The CTO of Silabs said: “Wireless is currently hard to use. We need to do more to make wireless as easy to use as a processor.” Kunbus, for example, showcased a wireless IO-Link system that utilizes two system-on-modules based on Texas Instruments CC265x and CC264x microcontrollers to enable communication between the I/O device and the sensors/actuators on the 2.4 GHz band, with a distance of 20 meters between them. Advantech showcased wireless I/O modules to transmit the sensor data directly to the SCADA system via Wi-Fi (WISE-4220), NB-IoT (Wise-4671), and LoRa (Wise-4610).
5. Advancements in RTOS technology
Real-time operating systems (RTOS) have become increasingly important at the intersection of constraint devices and real-time applications. RTOS are designed to provide a predictable and deterministic response time for time-sensitive tasks and can handle real-time events. The goal is to increase efficiency, reduce latency, and improve system stability. Segger Microcontroller GmbH, for example, showcased its latest RTOS solution embOS-Ultra, which replaces the traditional tick-based system of one millisecond with a clock-based scheduling that increases the resolution of the scheduling to microseconds(μs) or even nanoseconds (ns).
6. Chipset players are adopting the new Matter standard for smart homes
Matter is a relatively new application layer protocol designed for use in smart home devices. Vendors produce Matter-compliant devices that enable interoperability between different vendors. With Matter, the actual communication technology (e.g., Wi-Fi) does not matter (pun intended). Many chip companies, including ARM, NXP, Nordic Semiconductors, and Murata, have launched Matter-compliant wireless modules and MCUs for use in smart home devices to support widespread adoption of the protocol. For example, Murata has released the LBES5PL2EL module integrated with the IW612 chip from NXP, Nordic Semiconductors has introduced the nRF-7002 Dev kit with a Matter-compliant nRF5340 SoC, and NXP has announced the wireless tri-radio MCU RW612 and the K32W148 multi-protocol MCU.
7. Putting the legacy ISA-95 device-centric pyramid behind and moving to data-centric architectures
For years, the ISA-95 pyramid has served as a standard to describe different layers of hardware and connectivity. New communication protocols such as OPC UA and DDS promise to help in moving toward a more data-centric view of the architecture. At the fair, RTI presented its plans to prioritize the DDS protocol that treats all types of devices connected to the system equally, regardless of their specific characteristics. Meanwhile, the OPC Foundation shared that the device-agnostic OPC UA FX standards for field level devices are now stable on a controller-to-controller level, marking an important step forward in the development of this technology.
8. Vendors working toward making software-defined vehicles (SDVs) a reality
The automotive industry is witnessing a surge in the development of hardware and software solutions to enhance vehicles’ functionality and enable efficient operation management, which is leading to software-defined vehicles (SDVs). This trend is fueled by advancements in both hardware equipment and software applications. To cater to this growing demand, computing hardware maker Adlink demonstrated a proof-of-concept for autonomous driving using sensor fusion. The demonstration featured four tier IV C1 cameras and two Ouster OS1-32 LiDAR sensors that were connected to an AI-enabled autonomous driving system (AVA-3510) and a robotic controller (RQX-59). On top of new hardware solutions, there is a significant focus on developing software solutions to augment vehicle functionality. Companies such as Apex.AI, Green Hills Software, and Volkswagen’s software company CARIAD showcased their vision for the SDV. CARIAD’s “VW.OS” operating system, set to be released in 2025, is marketed to provide a reliable and secure platform for developing and deploying software applications on vehicles.
9. “Security by design” is becoming ever more important
As IoT devices become more complex and interconnected, ensuring security is becoming increasingly critical for building a secure future IoT ecosystem. Implementing security measures from the design phase can help prevent vulnerabilities and minimize risks throughout the device’s life cycle. By creating security by design, businesses can establish trust among consumers and unlock the full potential of IoT. At the fair, Eurotech emphasized its commitment to security at every stage of the device life cycle by partnering with AWS to offer certification-based authentication. Secure IC highlighted the critical need for hardware-based security at the chip level, firmware security, security life cycle management tools, and certifications. To ensure the security of IoT devices with a lifespan of 10–15 years, Crypto Quantique and WolfSSL demonstrated its post-quantum security solutions, which rely on quantum-driven hardware root of trust and hybridizing post-quantum algorithms, respectively.
10. Partnerships remain key due to rising complexity
As technology and solutions become more complex, companies are increasingly partnering with others to integrate their expertise and provide complementary services to customers. This is particularly evident with hardware, software, and security companies, who focus on providing end-to-end solutions together. For example, Infineon and Apex.AI are partnering to provide a development kit that enables faster integration of safety-critical automotive functions into future vehicles by using Infineon’s AURIX TC3X microcontroller. Qualcomm Technologies and Arrow Electronics expanded their collaboration by announcing the establishment of a dedicated Edge Lab that helps customers deploy machine vision, edge AI, and other use cases. The first outcome of the edge lab is the “Aikri 42x” development kit, which is based on Qualcomm‘s latest QRB4210 SoC.
Are you interested in learning more about IoT chipset and edge trends?
IoT Analytics is a leading global provider of market insights and strategic business intelligence for the Internet of Things (IoT), AI, Cloud, Edge, and Industry 4.0.
Embedded World 2023—the Latest IoT Chipset and Edge Trends
36-page report highlighting key insights from one of the world’s leading fairs for the embedded community.
Related publications
You may be interested in the following publications:
- Machine Vision Market Report 2022-2027
- Industrial AI and AIoT Market Report 2021–2026
- IoT Sensors Market Report 2022-2027
- Enterprise Augmented/Mixed Reality Market Report 2022–2027
- IoT Communication Protocols Adoption Report 2022
Related articles
You may also be interested in the following recent articles:
- Top 7 upcoming machine vision applications—enabled by recent advances in AI, cameras, and chips
- The rise of industrial AI and AIoT: 4 trends driving technology adoption
- 5 IoT sensor technologies to watch
- The enterprise AR market and the industrial metaverse: Why 2023 marks an inflection point
- 5 things to know about IoT protocols
Related market data
You may be interested in the following IoT market data products:
- Global Cellular IoT Connectivity Tracker & Forecast
- Global Cellular IoT Module and Chipset Market Tracker & Forecast
Are you interested in continued IoT coverage and updates?
Subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter to stay up-to-date on the latest trends shaping the IoT markets. For complete enterprise IoT coverage with access to all of IoT Analytics’ paid content & reports including dedicated analyst time check out Enterprise subscription.


