
Which are the hottest application areas for the Internet of Things right now?
IoT Analytics continues to track in which verticals most IoT projects are happening. The latest 2020 analysis shows that most IoT projects still happen in Manufacturing/Industrial settings, with verticals such as Transportation/Mobility, Energy, Retail and Healthcare having also increased their relative share in comparison to past analyses.
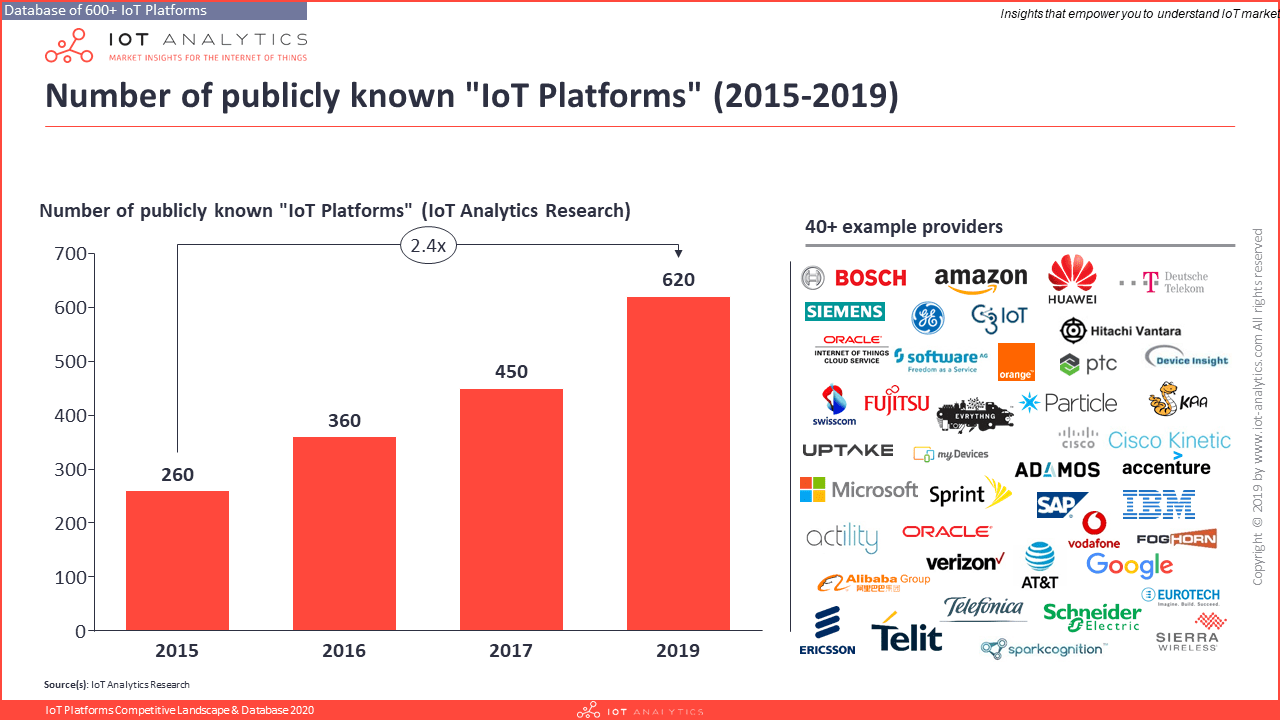
The 2020 analysis is based on 1,414 actual IoT projects that were explored as part of IoT Analytics’ research tracking IoT platforms and the underlying data is included in the 2020 list of 620 IoT platforms. The fact that more than 1,000 publicly announced IoT projects now make use of an IoT platform highlights the importance and pervasiveness of IoT platforms in bringing IoT solutions to market.
This article discusses selected IoT projects in each of the 10 application areas, including 20 examples of recent projects – stay tuned for more in-depth coverage of the top IoT use cases and more structured industry-specific deep-dives in the coming months.
(Note: The research presented in this article is confined to IoT projects that make use of an IoT Platform and does not include any consumer-focused IoT projects such as smart home, wearable devices or hobby projects).
Top 10 IoT application areas

(Note: The analysis methodology has changed slightly compared to past IoT Application analyses – in the past IoT Analytics looked at all known IoT projects, this time, due to the fast growth in number of IoT projects, IoT Analytics confined the analysis to the projects performed in conjunction with one of the 620 known providers of IoT platforms.)
The 2020 analysis of the top IoT application areas shows that of the 1,414 public enterprise IoT projects identified, Manufacturing / Industrial settings are most common (22%), followed by Transportation / Mobility (15%) and Energy IoT projects (14%).
For reference, see the IoT Analytics IoT applications analysis 2015 here and the 2018 analysis here.

1. IoT applications area #1: Manufacturing / Industrial
1a. Overview
Manufacturing / Industrial has taken over the top spot from “Cities” – the number one IoT application area in the 2018 analysis. Technology giants such as Microsoft and AWS as well as large industrial automation players such as Siemens or Rockwell Automation are among the driving forces of the digital transformation in the manufacturing / industrial industry.
“Industrial IoT is transforming the rules of manufacturing, fueling cloud and edge innovation, accelerating the evolution of digital factories, and enhancing operational performance.”
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, Nov 2019
“Manufacturers and industrial operators are discovering practical ways to apply IoT across their operations, and they’re deriving measurable business value as a result. Combining IoT technology and expertise in specific industrial applications enables better collaboration, faster problem-solving and increased productivity.”
Blake Moret, CEO of Rockwell Automation, May 2019
1b. Typical IoT Platform-enabled applications
The industrial IoT application area covers a wide range of connected “things” projects both inside and outside the factory. For example inside, many IoT-based factory automation and control projects include holistic smart factory solutions with numerous elements such as production floor monitoring, wearables and Augmented Reality on the shop-floor, remote PLC control, or automated quality control systems. Typical outside the factory projects include remote control of connected machinery, equipment monitoring, or management and control of entire remote industrial operations such as oil rigs. Many of the case studies mention “reducing operational downtime and cost saving” as the key drivers for OEMs to introduce industrial IoT solutions.
1c. Selected IoT Platform-enabled projects
Example 1: Howden Mixed Reality solutions. Howden, a Scottish manufacturer of air and gas handling solutions, turned to Microsoft and PTC to develop scalable mixed reality solutions that overlay real-time IoT data from connected products with 3D Augmented Reality experiences to provide step-by-step instructions on how to solve problems with the equipment. The solutions enable Howden’s customers to reduce the challenges and costs associated with unplanned downtime and better-align overall maintenance strategies—which were previously based only on conjecture and after-the-fact analysis. These innovations ultimately save customers a significant amount of time and associated cost.
Example 2: Severstal Asset Performance. Severstal, a Russian steel manufacturer, turned to GE to reduce unscheduled maintenance delays with Predix Asset Performance Management. The solution enhanced equipment reliability by 20% by means of constantly improving strategies of maintenance, reducing the costs of repair and maintenance scheduling, effectively reallocating resources, and decreasing production risks.

2. IoT applications area #2: Transportation / Mobility
2a. Overview
Transportation / Mobility is the second largest IoT application area in 2020. Tesla set the industry benchmark for connected cars when it launched the Model S in 2012, introducing the first over-the-air software update capabilities. Since then pretty much every car manufacturer has followed suit integrating similar IoT technologies.
“Connected solutions bring increased vehicle and construction equipment uptime for our customers, better safety for drivers, operators and other road users – and of course – less emissions of carbon dioxide. The first million connected assets at Volvo is only the start, we are committed to remain a leader in this field.”
Martin Lundstedt, CEO of the Volvo Group, Oct 2019
“At Honda Innovations, we’re witnessing a convergence of technologies that will transform mobility, create new business opportunities, and change the way we manufacture products. Our Honda Xcelerator program is designed for tech innovators who seek to transform the mobility experience and our Honda Developer Studio offers the best resources for developers and partners interested in connected car development.”
Nick Sugimoto, CEO of Honda Innovations, Apr 2019
2b. Typical IoT Platform-enabled applications
Typical applications within Transportation/Mobility include telematics and fleet management solutions that connect with the local operating system within the car for vehicle diagnostic/monitoring such as battery monitoring, tire pressure monitoring, driver monitoring or simply vehicle tracking.
2c. Selected IoT Platform-enabled projects
- Example 3: KWRL real-time fleet monitoring. KWRL Transportation Co-op runs a large-scale school bus fleet in Washington state, USA and uses Samsara’s wireless fleet tracking platform to coordinate routes and keep buses running on schedule. Real-time fleet monitoring supplies visibility into where buses are at any given moment, sensors track stop paddle and emergency light activation, engine fault code alerts are automatically decoded so team instantly determines criticality of faults, and complete route history is used to build smarter routes and plan fleet expansion.
- Example 4: OmniBus fleet operations optimization. OnniBus.com is a leading long-distance bus service in Finland, building a more streamlined and sustainable transport operation with Telia’s connected vehicle solution designed to optimize the operations of heavy equipment and reduce fuel consumption using real-time operating data.
- Example 5: Caledonian driver behavior tracking. Caledonian Logistics, based in Aberdeen, Scotland, specializes in the movement of palletized goods and uses MyGeotab for fleet monitoring and tracking driver behavior. A fleet dashboard shows a lead table of drivers diagnostics making them fully accountable for their actions and raises alerts if any abnormal activity occurs.

3. IoT applications area #3: Energy
3a. Overview
As worldwide energy consumption is expected to grow by 40% over the next 25 years, the need for smarter energy solutions has reached an all-time high. IoT is revolutionizing nearly every part of the energy industry from generation to transmission to distribution and changing how energy companies and customers interact. Both solution providers and energy companies themselves understand the need for and value of connected IoT solutions in the sector.
“Through IoT we’re looking to significantly enhance the productivity and scope of our advanced analytics capabilities to create greater economic value across Shell’s operations. IoT allows us to optimize our existing investments in data and cloud infrastructure while accelerating time to value of AI-based applications, so we can better serve our customers with even more agility and efficiency.”
Jay Crotts, CIO Shell Group, Sept 2019
“IoT exists, there’s nothing futuristic about it. Already today advanced sensors make it possible to monitor and communicate grid data. The information gathered by the sensors is transmitted to gateways and elaborated by data centers using machine learning algorithms with increasingly sophisticated models of data reading. This process brings enormous benefits in terms of grid efficiency.”
Fabio Veronese, Head of Infrastructure & Networks Digital Hub at Enel, Nov 2018
3b. Typical IoT Platform-enabled applications
Energy accounts for 11% of the identified projects, up from 10% in 2018. The majority of projects focus on energy distribution, grid optimization, remote asset monitoring and management, predictive maintenance and creating more transparency for better informed customers.
3c. Selected IoT Platform-enabled projects
- Example 6: Exelon’s wind power forecast model. American utility company, Exelon, optimizes wind forecasting accuracy with GE’s Predix Platform to achieve a 70% performance increase for their wind farms. GE’s data science team created a physical and statistical wind power forecast model based on historical data provided by Exelon. They incorporated diverse data sources and took into account seasonal or time-of-day effects, ran the analytics in Predix Cloud, and wrote back the results in seconds.
- Example 7: Enel’s enhanced grid reliability solutions. To improve grid reliability and reduce the occurrence of faults, Enel, an Italian multinational energy company, deployed the C3.ai Predictive Maintenance application for 5 control centers. The application uses AI to analyze real-time network sensor data, smart meter data, asset maintenance records, and weather data to predict feeder failure.

4. IoT applications area #4: Retail
4a. Overview
More and more retailers recognize that they can improve their cost-efficiency and in-store customer-experience through innovative IoT use cases. There is a rising interest for retailers to digitize stores and create smarter processes – retail now accounts for 9% of the identified projects, up from 5% in the 2018 analysis.
“The potential to gather data and put it to use more effectively is exciting. We’re learning how IoT can help us to work differently. We’re improving many of our processes, and we’re empowering our associates with better tools and technology.”
Doug McMillon, CEO Walmart, Oct 2018
“We are seeing the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies in the shape of voice-activated digital assistants with a high degree of automation, taking care of purchases through interfaces with retailers’ ordering systems.”
Tesco Bengaluru, CEO Sumit Mitra, Dec 2017
4b. Typical IoT Platform-enabled applications
Typical IoT in retail solutions include in-store digital signage, customer tracking and engagement, goods monitoring and inventory management and smart vending machines among others.
4c. Selected IoT Platform-enabled projects
- Example 8: nuMedia’s mixed reality solution. US-basednuMedia Innovations digital host solution, PRSONAS powered by Digi, is using mixed-reality technology that mimics human experiences to enhance customer experiences e.g., smart digital kiosks have interactive self-service holograms that act as virtual sales reps and product specialists on the store’s front lines. These holograms together with digital signage project a company’s brand personality to attract, automate, and analyze customer engagements.
- Example 9: Art of Shaving enhanced shopper insights. The Art of Shaving, a US retail business of high-end men’s shaving and skin care accessories, turned to RetailNext to compare store performance across its retail locations based on an accurate entrance traffic solution. The solution deployed reliable systems to review detailed metrics, KPIs and analyze conversion rates by store, readily identifying norms, trends, and outliers, and creating plans to capture opportunities.

5. IoT applications area #5: Cities
5a. Overview
Smart cities are growing and blossoming in all parts of the world. The IMD Smart City Index 2019, which focuses on how citizens perceive the scope and impact of efforts to make their cities smart – balancing “economic and technological aspects” with “humane dimensions”, put Singapore, Zurich and Oslo as the top 3 smartest cities in 2019, followed by Geneva, Copenhagen, Auckland, Taipei, Helsinki, Bilbao and Dusseldorf completing the top 10. More and more cities continue to embrace the smart city concept from a citizen’s perspective:
“My brief is to rethink the smart city from the ground up, meaning to rethink technology, IoT, data, and focusing on what it can do to serve the people”
Francesca Bria, CTO of Barcelona Smart City, Oct 2019
“Open IoT data is a central point for any city that is smart in its character. We are trying to make data available to the public — not only to ensure transparency — but also to make our citizens better informed.”
Winn Nielsen, Head of City Data, City of Copenhagen, Denmark, Nov 2019
The percentage of smart city projects is down from the 2018 analysis for a number of reasons such as long tender timelines, long lead time to get smart city projects started, and the need to navigate city politics. The CEO of an IoT Platform start-up, for example, recently shared with IoT Analytics that “Sometimes, smart city tender timelines are so long that start-ups can’t survive long enough to wait for the process to finish, so the process tends to be biased towards the largest vendors”.
5b. Typical IoT Platform-enabled applications
Typical IoT projects in Smart Cities include connected traffic (smart parking, traffic management), utilities (smart waste, lighting), public safety (video surveillance) and environmental monitoring (air pollution).
5c. Selected IoT Platform-enabled projects
- Example 10: Amsterdam smart LED lighting project. Amsterdam’s Smart Lighting scheme includes a deployment of 144 LED smart streetlights along with cameras and public WIFI network in Hoekenrodeplein square. The LED Lights can be controlled remotely and automatically adapt to different lighting conditions.
- Example 11: Singapore’s sensor data sharing platform. Singapore uses an integrated sensor platform, Smart Nation Sensor Platform, to collect, analyze, and share data from connected sensors and devices to improve urban planning, transportation and public safety in the island. Examples of data sources include residential meters, traffic counters, cameras and lampposts.

6. IoT applications area #6: Healthcare
6a. Overview
IoT has only slowly proliferated itself in healthcare. However, things look to be changing in light of the center of COVID-19 pandemic. Early data suggests that digital health solutions that relate to COVID-19 are surging. Demand for specific IoT health applications such as telehealth consultations, digital diagnostics, remote monitoring, and robot assistance is increasing. The pandemic has thrust the healthcare industry into the limelight and many C-suites are taking note:
“There is a huge applicability of technology, data, and communication methodologies to tackle the current pandemic and help improve healthcare solutions through telehealth and telemedicine. Demand is emerging across the globe, there is a growing number of patients being remotely treated globally, for example the number of online consults globally has gone up 50 to hundred times in many health systems already. These solutions are here to stay even after the current crisis”
Amit Phadnis, Chief Digital Officer GE Healthcare, May 2020
“The pandemic has told us how much patients benefit from technology and apps. It is a kind of turbo-boost to advance our efforts around digitization. My main learnings from the coronavirus crisis so far have been of a technical nature: we need more open and transparent communication to address structures and processes that are no longer working.”
Dr. Peter Gocke, Chief Digital Officer Charite Universitätsmedizin Berlin
6b. Typical IoT Platform-enabled applications
Typical healthcare IoT projects within hospitals/clinics include medical device monitoring, health team coordination, optimizing workflow operations while out-patient focused solutions include patient monitoring, assisted living, elderly care, and pain medication management among others.
6c. Selected IoT Platform-enabled projects
- Example 12: Medisanté remote patient monitoring. Medisanté are simplifying remote patient monitoring with continuous monitoring of assets connected to healthcare applications, including battery life and general health of devices, which allows personalized patient care anytime, anywhere and equips care teams with a near real-time view of the patient’s health and activities.
- Example 13: Medtronic connected pacemakers. Medtronic offers connected pacemakers which are small devices implanted in the chest or abdomen to treat patients whose hearts are beating too slowly or irregularly. The device gathers data such as transmission history, battery information, updates on physical activity and vitals tracking, and can stimulate the heart muscle with electricity pulses that restore the heart’s rhythm to a normal rate.

7. IoT applications area #7: Supply chain
7a. Overview
As supply chains extend more and more to the end customers, resulting in more intricate flows of goods that are more complex to deliver, logistics providers are increasingly integrating connected digital solutions to tackle the complexity. A recent survey by Kenco, a US logistics provider, found that 56% of supply chain professionals are currently or planning to invest in sensors/IoT; up from 42% in 2017, to look for more operational efficiencies in how their supply chains operate.
“The transformation of A.P. Moller – Maersk from a diversified conglomerate to becoming a focused, integrated and digitized global logistics company continues. In particular, usage of our digital services has increased significantly over the last year, with more and more customers beginning to explore options for remote management of their supply chains.”
Søren Skou, CEO of A.P. Moller – Maersk, May 2020
“DHL are integrating IoT innovations to build the digital supply chain of tomorrow today. This is changing the way we collect, analyze and use data and, ultimately, our ways of working at these sites. By monitoring operational activities in real time rather than retrospectively, we can interpret data more meaningfully, and immediately re-engineer processes or warehouse layouts to boost operational efficiency and address potential safety blind spots in a warehouse.”
Markus Voss, Chief Operating Officer of DHL Supply Chain. May 2019
7b. Typical IoT Platform-enabled applications
Typical supply chain IoT projects include asset tracking, condition monitoring (e.g., cold chain, medical goods), inventory and storage management, automated guided vehicles, connected workers, among others. The Covid-19 pandemic has highlighted the value of IoT tracking across the supply chain. Recent months have unfortunately shown the stark reality that even vital medical equipment and PPE can go out of stock as global supply chains are disrupted. This realization is expected to be a big driver for IoT tracking solutions in the supply chain to help companies stay in control, keep an overview, and react quickly.
7c. Selected IoT Platform-enabled projects
- Example 14: Rotterdam’s connected port. Rotterdam Port is using sensors throughout their expansive dock facility to continuously gather real-time data about air temperature, wind speed, relative humidity, turbidity and salinity of the water plus water flow and levels, tides and currents. The port even has “Digital Dolphins,” smart quay walls and sensor-equipped buoys, and is exploring connected container solutions to gather data and use artificial intelligence to predict more accurately what the best time is to moor and depart cargo ships at ports – to reduce waiting times and costs.
- Example 15: DHL smart pallet solutions. DHL is trialing smart pallets for real time shipment monitoring (e.g., embedded sensors to detect geo location, movement, delay, shock, temperature, etc).

8. IoT applications area #8: Agriculture
8a. Overview
In 2050, it is estimated that a population of almost 10 billion people will need up to 70 percent more food than we do today. One way to address this challenge is through smart agriculture. IoT sensors can help farmers make more informed decisions to achieve higher crop yield, better quality produce, and save costs by reducing the use of fertilizers and pesticides. Some CEOs see IoT as the main source of disruption for the agriculture industry:
“Agriculture needs something to drive growth in productivity and sustainable intensification of food production. We believe the internet of things is the basis of the future of agriculture.”
Ros Harvey, Managing Director of The Yield, Australian start-up working with Bosch to develop smart agricultural solutions. June 2019
“John Deere sees the adoption of information technologies and IoT services in agriculture as no less transformative than the introduction of self-propelled machines to farming a century ago. We believe that precision agricultural practices in use today are laying the foundation for the future of farming: a continually smart, evolving and more efficient farm.”
John May, CEO of John Deere, Mar 2017
8b. Typical IoT Platform-enabled applications
Typical smart agriculture projects include precision farming, livestock monitoring, irrigation management, and automated drones for surveying farms, mapping fields, spraying crops, etc. Analysis of the case studies suggests that innovative technologies such as LPWAN are paving the way for Smart Agriculture’s growth in the Internet of Things landscape. LPWAN supplies a range of features in terms of energy consumption and long-range transmission i.e., the main network requirements for key applications in the sector. LPWANs are ideal for gathering data about local agricultural conditions including weather, soil moisture, chemical compositions of the soil and other environmental conditions at a much lower total cost of ownership. Furthermore, LPWANs make it possible to expand per-acre coverage and monitor more assets due to the simplicity of deployment and cost of ownership reductions.
8c. Selected IoT Platform-enabled projects
- Example 16: Kwekerij connected greenhouses.“We get so much insight into the temperature of our peppers during the growth phase, and can adjust the greenhouse climate accordingly. Based on this information, we can continually improve the quality of our produce, while cutting energy costs”- Sander Berkers, Supervisor at Kwekerij Moors Pepper Farm, Netherlands, Jan 2019
- Example 17: Hake connected dairy farm solutions. “When I get up in the morning and put on my boots, I don’t go to the stables first, I check my PC for alerts and I’m in the know right away. That’s what makes IoT technology so helpful. When a cow is in heat or eats less than anticipated because she starts coming down sick, there is a warning indicator for me. And that’s a great thing.” Steffen Hake, Dairy farmer in Wagenfeld-Ströhen, Germany, Aug 2015

9. IoT applications area #9: Buildings
9a. Overview
As part of the 2019 Energy Efficiency Indicator study Johnson Controls surveyed 400 energy and facility management executives in the United States and found that 71 percent of organizations invested in smart building control system improvements and over half have implemented an enterprise-wide smart building management system. Most new innovative connected solutions aim to increase productivity and efficiency while reducing operational costs through complete building life cycle management.
“Buildings have been there for thousands of years, but unaware if someone were to enter or leave them. With digitalization and IoT, a building can now get to know about its occupants. It can provide feedback, not only to the residents, but also to the facility managers and the owners. So to me, a smart building is one that doesn’t just stand there, but one that understands its environment, interacts, learns and adapts.”
Cedrik Neike, CEO of Siemens Smart Infrastructure, Oct 2019
“Real estate owners and managers are always seeking ways to reduce costs and increase tenant satisfaction. We believe that putting intelligence into the building that improves facilities management and analyzes how occupants and visitors use the building is the best way to fulfill their needs. We’re employing digitalization, AI, and Internet of Things technologies to optimize usage at every level and make the building a pleasant place to work, visit, and live.”
Michael Cesarz, CEO for MULTI at thyssenkrupp Elevator, Sept 2018.
9b. Typical IoT Platform-enabled applications
Typical connected building projects involve facility-automation and monitoring for building systems (HVAC, lighting, elevators, smoke alarms, fire extinguishers), building utilization and security (room use, access, surveillance).
9c. Selected IoT Platform-enabled projects
- Example 18: thyssenkrupp connected elevator solutions. At its Innovation Test Tower in Rottweil, Germany, thyssenkrupp Elevator is using Willow Twin, a digitalized virtual model of the physical building, to revolutionize the way buildings are maintained and to enhance the experience of tenants and visitors.
- Example 19: Connected shopping centre in Finland. A shopping centre in the Leppävaara district of Espoo, Finland is using Navigator software, from Siemens and eggsunimedia, to monitor and analyze the ventilation systems, room sensors and lighting systems in the multitude of premises and shops. The shopping centre was able to save 680 MWh of electricity and 800 MWh in centre heating, which is about half of the previous year’s consumption and cut energy costs by around €110,000.

10. IoT applications area #10: Other
10a. Overview
There are only a few (3%) projects that have been identified that are not part of the other 9 categories.
10b. Typical IoT Platform-enabled applications
Example IoT Platform-enabled projects in the Other area include those in hospitality, enterprise, finance, and sports.
10c. Selected IoT Platform-enabled project
Example 20: Cybex connected exercise equipment. “Our customers invest in our catalog of products for our reputation for developing innovative and reliable equipment that enhances human performance. We are furthering that reputation, and our customer’s success, by offering an Internet-based monitoring system that helps owners maximize the benefit of our products.” Lisa Juris, Chief Marketing Officer Cybex International. Cybex International offers premium exercise equipment used in fitness facilities worldwide. Gym owners regularly service their treadmills to ensure they stay up and running so Cybex developed a web-based asset management system to provide gym owners with real-time data on the status of each treadmill.
Methodology
The data presented in this article is partially based on IoT Analytics research on IoT platforms, performed in Q4/2019. As part of a wider research project on IoT platforms, IoT Analytics mined the websites of 620 IoT platform vendors in regards to documented IoT case studies and aggregated the data for each segment to come up with the top 10 applications areas based on real IoT projects.
Scope: The research focused on enterprise IoT solutions that are either directly employed by enterprises or sold to enterprises, thus excluding consumer-only cases such as wearables, smart home or hobbyist projects.
More information and further reading
The findings discussed in this article are derived from analysis of the List Of 620 IoT Platform Companies.
A sample of the report can be downloaded here:
Related articles
Related research
Existing research on IoT Platforms
- 2021 List of IoT Platform Companies
- IoT Platforms Market Report 2018-2023
- IIoT Platforms for Manufacturing 2019-2024
- IoT Platforms Vendor Comparison 2018
- IoT Platforms End-user Satisfaction Report 2019
Existing research on Industrial IoT
- IoT Commercialization & Business Model Report
- Equipment as a Service Market Report 2020-2025
- Industry 4.0 & Smart Manufacturing Adoption
- Industrial AI Market Report 2020-2025
Existing research on Smart Cities
- Smart City Use Cases & Technology Report 2020 – and in-depth look at 50 cities and how they are implementing IoT
- Smart City Market Report – a comprehensive look at the entire Smart City market incl. competitive landscape, and market sizing
Are you interested in continued IoT coverage and updates?
Subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter to stay up-to-date on the latest trends shaping the IoT markets. For complete enterprise IoT coverage with access to all of IoT Analytics’ paid content & reports including dedicated analyst time check out Enterprise subscription.

