In short
- According to the IoT Gateway Market Report 2023–2027, the $810-million telematics gateways market experienced accelerated growth following the COVID-19 pandemic and is expected to rise to a CAGR of 19% through 2027.
- Telematics gateways enable supply chain visibility by connecting vehicles and their sensors to external networks or the cloud, allowing for real-time tracking, predictive vehicle and fleet maintenance, route optimization, greater operational efficiency, and increased safety for drivers and the public.
- Telematics gateways have evolved through three generations—legacy, smart, and intelligent—based on advances in their hardware, e.g., multicore processors or GPUs/NPUs for AI integration.
Why it matters?
- For telematics vendors: Understand current trends comprehensively and anticipate future shifts in the telematics gateway market.
- For adopters and end-users: Learn about the advancements in telematics gateways and how they can benefit your operations, including real-time tracking and analytics, greater operational efficiency, and predictive maintenance for increased vehicle life cycles.
Market snapshot
The telematics gateways market accelerated to $810 million in 2022 and is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 19% from 2022 to 2027, according to the recently released IoT Gateway Market Report 2023–2027. Propelling this growth is the need for greater supply chain visibility, especially following the supply chain issues following the COVID-19 pandemic. Further, advancements in telematics gateways have helped companies optimize routing for greater efficiency, monitor fleet health, predict maintenance, and improve overall safety for drivers and the public.
As part of our analysis of IoT gateway trends, we recently discussed industrial IoT gateways and their vital role in bridging the IT and OT worlds. In this article, we will look at the role telematics gateways play in supply chain visibility and management, their evolution since the late 20th century, and their market outlook.
The insights in this article are based on the recently published 221-page
IoT Gateway Market Report 2023–2027
Download a sample to learn more about the report structure, select definitions, select market data, additional data points, and trends.
Already a subscriber?
Browse your dashboard here →
The role of telematics gateways
Telematics gateways play a vital role in connecting modes of transportation—including cars, trucks, trains, and ships—with an external network. Samsara, a top 5 telematics gateways vendor by market share according to our assessment, defines telematics as “the convergence of telecommunications and information processing” and notes that it is based on the French word télématique.
Much like how industrial IoT gateways are developed to connect various factory OT equipment to a company’s IT network or cloud, telematics gateways are designed for long-distance transmission of information, connecting remote equipment, such as vehicles, to centralized servers or the cloud. This allows companies to collect vehicle location and driver behavior data and data that can help optimize routes and predict maintenance needs.
Historically, telematics gateways shared information over cellular networks, with newer models leveraging greater connectivity speeds to share more and more data about vehicles and work environments. However, the growth of commercial satellite companies has made satellite connectivity a viable and affordable option for companies as well.
In the context of the supply chain issues that plagued the world economy following the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, telematics gateways have become essential for companies in managing their fleets, scheduling maintenance, and planning logistics/routing—all instrumental in a healthy supply chain. However, telematics gateways saw their beginning well before the pandemic—even before the turn of the millennium—and as computational and wireless technologies have evolved, so too have the capabilities of these gateways.
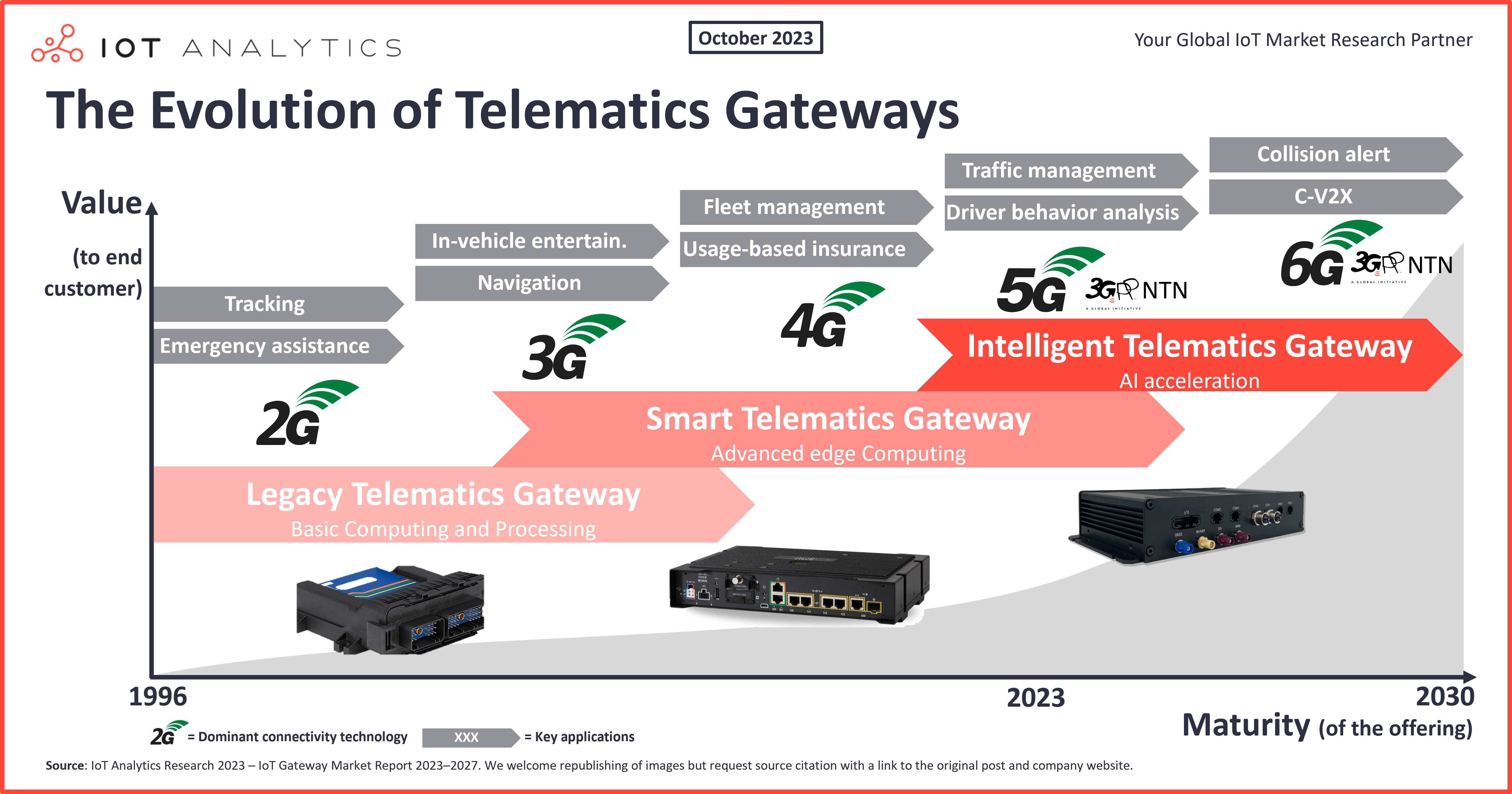
Evolution of telematics gateways
We are currently witnessing the advent of the intelligence telematics gateway generation…
From our perspective, the evolution of telematics gateways has progressed through three generations—legacy, smart, and intelligent—each representing computational capabilities. These generations overlay five distinct connectivity advancements (e.g., the transition from 3G to 4G connectivity) that have propelled the applications and data-sharing capabilities for the gateways.
We are currently witnessing the advent of the intelligent telematics gateway generation, where parallel or neural processing chips enable AI integration and real-time data processing and storage, with 5G connectivity at the helm. With 6G connectivity on the horizon, data sharing and analytics will be even faster, further bolstering AI’s real-time capabilities. With this, we anticipate being fully within the intelligent generation within the next decade.
Though devices to track and communicate with vehicles existed before telematics gateways, those devices were often single purpose. The demand to connect various tracking and vehicle sensors and compile the data for secure transmission and analytics spurred the development and growth of these gateways. With that, the following is a look at the evolution of these gateways, including their applications and examples.
First generation: Legacy telematics gateways
The first generation of telematics gateways, which we term legacy telematics gateways, were simple compared to the capabilities of telematics gateways today. They relied on 2G and, eventually, 3G and 4G connectivity, and they were designed—by connectivity limitation—for low-data-requirement applications. They primarily consisted of a cellular modem to send basic locational and environmental data and offer emergency and theft recovery assistance.
The revenue share of these legacy gateways is dominant today, but we forecast this share to shrink to 49% of all telematics gateways in use by 2027. For the foreseeable future, legacy telematics gateways will still provide cost-effective options for companies looking for basic telematics data without requiring edge computing or heavy data-sharing loads.
Legacy telematics gateway example: The NEXCOM FMS 1000 had data acquisition and 2G/3G communication features to help managers keep track of heavy machinery for oil and gas, logging, construction, and mining industries. With these industries in mind, NEXCOM gave it a rugged form factor to match field conditions.

Second generation: Smart telematics gateways
As semiconductors advanced—enabling greater processing, memory, and storage capabilities—vendors began fielding smart telematics gateways capable of real-time data analytics closer to the edge, either in the vehicles they were equipped in or in field operations centers. Further, the progression from 3G to 4G and 5G connectivity enabled greater real-time sharing of large amounts of data (such as live video feeds and safety data from the vehicles to the ops centers or analytics and routing data from the ops centers to the vehicles) and faster decision-making. Further, the growth in the commercialization of space has allowed for even more remote connectivity.
Our analysis forecasts the revenue share of this generation of gateways will grow to 25% of the telematics gateways market by 2027, though decelerating along the way as intelligent telematics gateways become more available and affordable. Companies that demand edge computing options without heavy data-sharing needs will find utility in these smart telematic gateways even as the market trends toward gateways with more robust edge and data-sharing capabilities.
Smart telematics gateway example: Cisco Catalyst IR1800 Rugged Series, released in 2021, is a versatile 5G telematics gateway with built-in edge security and computation capabilities to run applications.
Case study: Cisco’s Catalyst IR1800 Rugged Series provides wireless connectivity for law enforcement vehicles

Problem: Law enforcement officers need fast access to the same real-time data and applications that they have at their stations. However, police cruisers have complex needs, including reliable and secure communication, connectivity for moving vehicles in extreme conditions, high bandwidth inside and outside the car, and the ability to track vehicles in remote incident areas.
Solution: Telematics gateways that not only connect various law enforcement devices and send the data (along with location) to stations but also deliver the data that law enforcement officers need in real time.
Cisco provides one such solution, including secure 5G gateways and Wi-Fi access points. These solutions can connect multiple devices, including laptops, cameras, license plate readers, electronic citation systems, tablets, body cams, and smartphones. Further, by using this solution, law enforcement can stream live video from cruisers to the station and track vehicles in remote incident areas.
Third generation: Intelligent telematics gateways
“The next generation of fleet-management systems providers are already offering edge computing. By adopting technology that’s faster, more reliable, more secure and more affordable, fleets can focus on what truly matters — running their businesses and moving freight.”
– Ken Evans, Founder and CEO of Konexial (in a Think Tank piece on SupplyChainBrain)
The rise in interest in AI spurred the transition to intelligent telematics gateways. These gateways are embedded with powerful processors, such as multicore CPUs, and can handle data processing, analytics, and AI interfacing at the farthest edge for real-time decision-making. They have ample memory and storage space for caching data, running AI models, and storing historical data. Some models have dedicated AI hardware accelerators, such as GPUs or neural processing units (NPUs), for efficient AI model execution.
With AI integration, managers and operations can see the following benefits:
- Real-time decision-making: AI can process large amounts of data in real-time, allowing quicker responses to emergent situations.
- Predictive maintenance: AI can analyze data from vehicle sensors to predict when parts might fail, preventing costly breakdowns and extending vehicle life.
- Improve driver and public safety: AI can identify unsafe behaviors by analyzing driving patterns and prompting corrective actions or alerts.
- Enhanced efficiency: AI algorithms can optimize routes for fuel efficiency and traffic avoidance, leading to reduced costs and better time management.
Based on our analytical projections, the revenue share for these intelligent gateway systems may accelerate to 26% of the telematics gateways market, translating to an estimated $509 million. Though this is below the forecasted revenue share for the other generations, the technology is new, and AI is a hot topic for many companies. Further, we expect the desire for greater operational efficiency and the likely passing of green regulations to accelerate demand for AI-integrated, intelligent telematics gateways.
Intelligent telematics gateway example: Eurotech’s DynaGATE 10-14, released in 2022, is a 5G telematics gateway embedded with NXP i.MX 8M Plus, CPU, integrated NPU, and 2D/3D GPU that can process IP and GMSL2 video feeds from vehicle cameras.

Market wrap-up and outlook
We forecast the telematics gateways market to grow at 19.3% CAGR from 2022 to 2027, driven by demands of supply chain visibility, fleet optimization, operational efficiency, and safety. The legacy telematics gateways’ market share is declining and will continue to give way to an accelerating growth for intelligent telematics gateways and a decelerating growth for smart telematics gateways.
The future of telematics gateways looks promising due to AI adoption, the growth of connected vehicles, and the need for enhanced device security. The integration of 5G and, eventually, 6G connectivity will drive the development of new applications, likely spurring increased demand in emerging markets. In short, the market’s future lies in intelligent telematics gateways.
What it means for telematics gateway vendors
5 questions that telematic gateway vendors should ask themselves based on insights in this article:
- How does our product portfolio align with the evolving generations of telematics gateways, and are we prepared for the rise of intelligent gateways?
- Given the projected growth, what investments should we be making now in R&D to remain competitive, especially in the domain of AI integration?
- How does our current revenue and market positioning compare to the projections made in the report?
- What strategies can we implement to ensure our legacy products remain relevant and competitive, given their anticipated lasting demand?
- The article mentions several competitors like Samsara and Eurotech. How does our product stack up against theirs, both in terms of features and market penetration?
What it means for fleet operators
5 questions that fleet operators should ask themselves based on insights in this article:
- Is our fleet currently leveraging the latest telematics gateway technologies, and if not, where are we in the spectrum of legacy, smart, and intelligent gateways?
- Considering the increasing importance of supply chain visibility, how can we use telematics gateways to ensure we have real-time data and visibility over our fleet operations?
- How can we leverage the benefits of AI integration in our fleet operations, especially in areas like predictive maintenance, real-time decision-making, and route optimization?
- Given the advancements in telematics gateways, do we have a strategy in place for upgrading our existing systems, or should we look into partnerships with leading vendors?
- Are there potential cost-saving opportunities in transitioning from our current gateway setup to more advanced, AI-integrated systems?
More information and further reading
Are you interested in learning more about the IoT gateway market?
IoT Gateway Market Report 2023–2027
A 221-page IoT Gateway Market Report 2023–2027, including detailed definitions of IoT gateways, market projections, adoption drivers, competitive landscape, notable trends, and case studies.
Already a subscriber?
Browse your dashboard here →
Related publications
You may also be interested in the following reports:
- Global Cloud Projects Report and Database 2023
- IoT Sensors Market Report 2022-2027
- Embedded World 2023—the Latest IoT Chipset and Edge Trends
- Enterprise Augmented/Mixed Reality Market Report 2022–2027
- SPS Fair 2022—the latest industrial automation trends
- Machine Vision Market Report 2022-2027
- Industrial Edge Computing Market Report
- Digital Supply Chain Market Report 2022–2027
Related dashboard and trackers
You may also be interested in the following dashboards and trackers:
- Global Cellular IoT Connectivity Tracker & Forecast
- Global Cellular IoT Module and Chipset Market Tracker & Forecast
- Global IoT eSIM Modules and iSIM Chipsets Market Tracker
- Global IoT Enterprise Spending Dashboard
Related articles
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- Mapping 7,000 global cloud projects: AWS vs. Microsoft vs. Google vs. Oracle vs. Alibaba
- 5 IoT sensor technologies to watch
- The top 10 IoT chipset and edge trends—as showcased at Embedded World 2023
- The top 10 IT/OT convergence trends—as showcased at SPS fair 2022
- 8 key technologies transforming the future of global supply chains
Subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter to stay up-to-date on the latest trends shaping the IoT markets. For complete enterprise IoT coverage with access to all of IoT Analytics’ paid content & reports including dedicated analyst time check out Enterprise subscription.


